
PROFILE
OFFICIAL NAME:
Republic of Kenya
Geography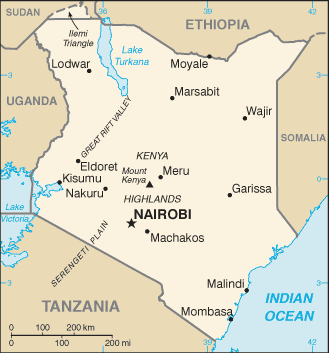
Area: 582,646 sq. km. (224,960 sq mi.); slightly
smaller than Texas.
Cities: Capital--Nairobi
(pop. 2.9 million; 2007 est.). Other
cities--Mombasa (828,500; 2006 est.), Kisumu
(322,000; 1999), Nakuru (219,366; 1999), Eldoret
(193,830; 1999).
Terrain: Kenya rises from a low coastal plain on
the Indian Ocean in a series of mountain ridges
and plateaus which stand above 3,000 meters
(9,000 ft.) in the center of the country. The
Rift Valley bisects the country above Nairobi,
opening up to a broad arid plain in the north.
Highlands cover the south before descending to
the shores of Lake Victoria in the west.
Climate: Tropical in south, west, and central
regions; arid and semi-arid in the north and the
northeast.
People
Nationality: Noun
and adjective--Kenyan(s).
Population (June 2007 est.): 37.9 million.
Major ethnic groups: Kikuyu 22%, Luyia 14%, Luo
14%, Kalenjin 11%, Kamba 11%, Kisii 6%, Meru 5%.
Religions: Christian 80%, Muslim 10%,
traditional African religions 9%,
Hindu/Sikh/Baha'i/Jewish 1%.
Languages: English (official), Swahili
(national), over 40 other languages from the
Bantu, Nilotic, and Cushitic linguistic groups.
Education: First 8 years of primary school are
provided tuition-free by the government. In
January 2008, the government began offering a
program of free secondary education, subject to
some restrictions.Attendance--92% for
primary grades. Adult
literacy rate--85.1%.
Health: Infant
mortality rate--57.4/1,000. Life
expectancy--55.3 yrs (2007 est.).
Work force (1.95 million wage earners): public
sector 30%; private sector 70%. Informal
sector workers--6.4 million. Services--45%; industry
and commerce--35%; agriculture--20%.
Government
Type: Republic.
Independence: December 12, 1963.
Constitution: 1963.
Branches: Executive--president
(chief of state, commander in chief of armed
forces), prime minister (head of government),
and two deputy prime ministers. Legislative--unicameral
National Assembly (parliament). Judicial--Court
of Appeal, High Court, various lower and special
courts, includes Kadhi (Sharia) courts.
Administrative subdivisions: 69 districts,
joined to form 7 rural provinces. The Nairobi
area has special provincial status. The
government has gazetted 37 new districts. The
process of establishing these districts is
ongoing.
Political parties: Over 100 registered political
parties. Two coalitions, the Party of National
Unity (PNU) and the Orange Democratic Movement (ODM),
dominate the political party scene. PNU
membership is filled by parties representing
Kikuyu and closely related ethnic groups; ODM
membership ranks are filled by parties
representing nearly everybody else. PNU and ODM
agreed in February 2008 to form a grand
coalition government in a power-sharing
arrangement that ended the political crisis
erupting after highly controversial national
elections in December 2007.
Suffrage: Universal at 18.
Economy
GDP (2007 est.): $29.3 billion.
Annual growth rate (2006): 6.1%.
Gross national income per capita (2006): $455.
Natural resources: Wildlife, soda ash, land.
Agriculture: Products--tea,
coffee, sugarcane, horticultural products, corn,
wheat, rice, sisal, pineapples, pyrethrum, dairy
products, meat and meat products, hides, skins. Arable
land--5%.
Industry: Types--petroleum
products, grain and sugar milling, cement, beer,
soft drinks, textiles, vehicle assembly, paper
and light manufacturing.
Trade (2006): Exports--$3.1
billion: tea, coffee, horticultural products,
petroleum products, cement, pyrethrum, soda ash,
sisal, hides and skins, fluorspar. Major
markets--Uganda, Tanzania, United Kingdom,
Germany, Netherlands, Ethiopia, Rwanda, Egypt,
South Africa, United States. Imports--$7.2
billion: machinery, vehicles, crude petroleum,
iron and steel, resins and plastic materials,
refined petroleum products, pharmaceuticals,
paper and paper products, fertilizers, wheat. Major
suppliers--U.K., Japan, South Africa,
Germany, United Arab Emirates, Italy, India,
France, United States, Saudi Arabia.
PEOPLE
Kenya has a very diverse population that
includes three of Africa's major sociolinguistic
groups: Bantu (67%), Nilotic (30%), and Cushitic
(3%). Kenyans are deeply religious. About 80% of
Kenyans are Christian, 10% Muslim, and 10%
follow traditional African religions or other
faiths. Most city residents retain links with
their rural, extended families and leave the
city periodically to help work on the family
farm. About 75% of the work force is engaged in
agriculture, mainly as subsistence farmers. The
national motto of Kenya is Harambee,
meaning "pull together." In that spirit,
volunteers in hundreds of communities build
schools, clinics, and other facilities each year
and collect funds to send students abroad. The
six state universities enroll about 45,000
students, representing some 25% of the Kenyan
students who qualify for admission. There are
six private universities.
HISTORY
Fossils found in East Africa suggest that
protohumans roamed the area more than 20 million
years ago. Recent finds near Kenya's Lake
Turkana indicate that hominids lived in the area
2.6 million years ago.
Cushitic-speaking people from what is now Sudan
and Ethiopia moved into the area that is now
Kenya beginning around 2000 BC. Arab traders
began frequenting the Kenya coast around the
first century AD. Kenya's proximity to the
Arabian Peninsula invited colonization, and Arab
and Persian settlements sprouted along the coast
by the eighth century. During the first
millennium AD, Nilotic and Bantu peoples moved
into the region, and the latter now comprise two
thirds of Kenya's population. The Swahili
language, a Bantu language with significant
Arabic vocabulary, developed as a trade language
for the region.
Arab dominance on the coast was interrupted for
about 150 years following the arrival of the
Portuguese in 1498. British exploration of East
Africa in the mid-1800s eventually led to the
establishment of Britain's East African
Protectorate in 1895. The Protectorate promoted
settlement of the fertile central highlands by
Europeans, dispossessing the Kikuyu and others
of their land. Some fertile and well watered
parts of the Rift Valley inhabited by the Maasai
and the western highlands inhabited by the
Kalenjin were also handed over to European
settlers. For other Kenyan communities, the
British presence was slight, especially in the
arid northern half of the country. The settlers
were allowed a voice in government even before
Kenya was officially made a British colony in
1920, but Africans were prohibited from direct
political participation until 1944 when a few
appointed (but not elected) African
representatives were permitted to sit in the
legislature.
From 1952 to 1959, Kenya was under a state of
emergency arising from the "Mau Mau" insurgency
against British colonial rule in general and its
land policies in particular. This rebellion took
place almost exclusively in the highlands of
central Kenya among the Kikuyu people. Tens of
thousands of Kikuyu died in the fighting or in
the detention camps and restricted villages.
British losses were about 650. During this
period, African participation in the political
process increased rapidly.
The first direct elections for Africans to the
Legislative Council took place in 1957. Kenya
became independent on December 12, 1963, and the
next year joined the Commonwealth. Jomo
Kenyatta, an ethnic Kikuyu and head of the Kenya
African National Union (KANU), became Kenya's
first President. The minority party, Kenya
African Democratic Union (KADU), representing a
coalition of small ethnic groups that had feared
dominance by larger ones, dissolved itself in
1964 and joined KANU.
A small but significant leftist opposition
party, the Kenya People's Union (KPU), was
formed in 1966, led by Jaramogi Oginga Odinga, a
former Vice President and Luo elder. The KPU was
banned shortly thereafter, however, and its
leader detained. KANU became Kenya's sole
political party. At Kenyatta's death in August
1978, Vice President Daniel arap Moi, a Kalenjin
from Rift Valley province, became interim
President. By October of that year, Moi became
President formally after he was elected head of
KANU and designated its sole nominee for the
presidential election.
In June 1982, the National Assembly amended the
constitution, making Kenya officially a
one-party state. Two months later, young
military officers in league with some opposition
elements attempted to overthrow the government
in a violent but ultimately unsuccessful coup.
In response to street protests and donor
pressure, Parliament repealed the one-party
section of the constitution in December 1991. In
1992, independent Kenya's first multiparty
elections were held. Divisions in the opposition
contributed to Moi's retention of the presidency
in 1992 and again in the 1997 election.
Following the 1997 election Kenya experienced
its first coalition government as KANU was
forced to cobble together a majority by bringing
into government a few minor parties.
In October 2002, a coalition of opposition
parties formed the National Rainbow Coalition
(NARC). In December 2002, the NARC candidate,
Mwai Kibaki, was elected the country's third
President. President Kibaki received 62% of the
vote, and NARC also won 59% of the parliamentary
seats. Kibaki, a Kikuyu from Central province,
had served as a member of parliament since
Kenya's independence in 1963. He served in
senior posts in both the Kenyatta and Moi
governments, including Vice President and
Finance Minister. In 2003, internal conflicts
disrupted the NARC government. These conflicts
came into the open when the government put its
draft constitution to a public referendum. Key
government ministers organized the opposition to
the draft constitution, which was defeated
soundly. Two principal leaders of the movement
to defeat the draft constitution, Raila Odinga
and Kalonzo Musyoka--both former Kibaki
allies--were presidential candidates for the
Orange Democratic Movement (ODM) party and the
Orange Democratic Movement-Kenya (ODM-K) party,
respectively. In September 2007, President
Kibaki and his allies formed the coalition Party
of National Unity (PNU). KANU joined the PNU
coalition, although it served in parliament as
the official opposition party.
On December 27, 2007, Kenya held presidential,
parliamentary, and local government elections.
While the parliamentary and local government
elections were largely credible, the
presidential election was seriously flawed, with
irregularities in the vote tabulation process as
well as turnout in excess of 100% in some
constituencies. On December 30, the chairman of
the Electoral Commission of Kenya declared
incumbent Mwai Kibaki as the winner of the
presidential election. Violence erupted in
different parts of Kenya as supporters of
opposition candidate Raila Odinga and supporters
of Kibaki clashed with police and each other.
The post-election crisis left more than 1,000
Kenyans dead and about 600,000 people became
refugees or were internally displaced. In order
to resolve the crisis, negotiation teams
representing PNU and ODM began talks under the
auspices of former UN Secretary General Kofi
Annan and the Panel of Eminent African Persons
(Benjamin Mkapa of Tanzania and Graca Machel of
Mozambique). On February 28, 2008, President
Kibaki and Raila Odinga signed a power-sharing
agreement, which provided for the establishment
of a prime minister position (to be filled by
Odinga) and two deputy prime minister positions,
as well as the division of cabinet posts
according to the parties' proportional
representation in parliament. On March 18, 2008,
the Kenyan parliament amended the constitution
and adopted legislation to give legal force to
the agreement. On April 17, 2008 the new
coalition cabinet and Prime Minister Odinga were
sworn in. Negotiations are ongoing regarding
longer-term reform issues, including
constitutional reform, land tenure reform,
judicial reform, and the need to address poverty
and inequality.
GOVERNMENT
The unicameral National Assembly consists of 210
members elected to a term of 5 years from
single-member constituencies, plus 12 members
nominated by political parties on a proportional
representation basis. The president appoints the
vice president; under the power-sharing
agreement, the president with the agreement of
the prime minister makes the initial appointment
of cabinet members from among those elected to
the assembly. Subsequent cabinet appointments
are made by the president in consultation with
the prime minister, in accord with the
power-sharing agreement's proportional division
of cabinet positions. The attorney general and
the speaker are ex-officio members of the
National Assembly.
The judiciary is headed by a High Court,
consisting of a Chief Justice and High Court
judges and judges of Kenya's Court of Appeal,
all appointed by the president.
Local administration is divided among 69 rural
districts, each headed by a commissioner
appointed by the president. The government has
proposed 37 more districts, but these are not
yet ratified by parliament. The districts are
joined to form seven rural provinces. Nairobi
has special provincial status. The Ministry of
State in charge of Provincial Administration and
Internal Security supervises the administration
of districts and provinces.
Principal Government Officials
President--Mwai Kibaki
Vice President--Kalonzo Musyoka
Prime Minister--Raila Odinga
Minister of Foreign Affairs--Moses Wetangula
Ambassador to the United States--Peter Ogego
Ambassador to the United Nations--Zachary
Muita-Muburi
Consulate General Los Angeles--Ms. Nyambura
Kamau
Kenya maintains an embassy in the United States
at 2249 R Street NW, Washington, DC 20008 (tel.
202-387-6101, website: http://www.kenyaembassy.com)
and consulates in Los Angeles and New York.
POLITICAL CONDITIONS
Until post-election political unrest struck in
early 2008, Kenya had, since independence,
maintained remarkable stability despite changes
in its political system and crises in
neighboring countries. This had been
particularly true since the re-emergence of
multiparty democracy and the accompanying
increase in freedom (including freedom of
speech, the press, and assembly).
In December 2002, Kenyans held democratic and
open elections, which were judged free and fair
by international observers. The 2002 elections
marked an important turning point in Kenya's
democratic evolution as the presidency and the
parliamentary majority passed from the party
that had ruled Kenya since independence to a
coalition of new political parties. The
government lost a referendum over its draft
constitution in November 2005. This vote too was
widely accepted as free, fair, and credible.
Under the first presidency of Mwai Kibaki, the
NARC coalition promised to focus its efforts on
generating economic growth, improving and
expanding education, combating corruption, and
rewriting the constitution. The first two goals
were largely met, but progress toward the second
two goals was limited. President Kibaki's
cabinet from 2002-2005 consisted of members of
parliament from allied parties and others
recruited from opposition parties who joined the
cabinet without the approval of their party
leaderships.
In early 2006, revelations from investigative
reports of two major government-linked
corruption scandals rocked Kenya and led to
resignations, including three ministers (one of
whom was later re-appointed). In March 2006,
another major scandal was uncovered involving
money laundering and tax evasion in the Kenyan
banking system. The government's March 2006 raid
on the Standard Group media house conducted by
masked Kenyan police was internationally
condemned and was met with outrage by Kenya
media and civil society. The government did not
provide a sufficient explanation. No one has
been held accountable.
The December 2007 elections were marred by
serious irregularities, and set off a wave of
violence throughout Kenya. Following the
February 2008 signing of a power-sharing
agreement between President Kibaki and the
opposition, a new coalition cabinet was sworn in
April 2008, headed by Prime Minister Odinga. The
42-member cabinet is the largest in Kenya's
history and includes new ministries for
cooperative development, Northern Kenya
development, and Nairobi metropolitan
development. Several ministries were also
subdivided, creating a number of new cabinet
positions.
With the creation of the coalition government,
the Kenyan Government will focus its attention
on achieving its ambitious reform agenda, aimed
at avoiding a repeat of early 2008's
post-election political and tribal violence. The
government also plans to draft a new
constitution by April 2009, specifically to
address land rights issues and to restructure
the government by strengthening institutions to
create a more effective system of checks and
balances.
ECONOMY
After independence, Kenya promoted rapid
economic growth through public investment,
encouragement of smallholder agricultural
production, and incentives for private (often
foreign) industrial investment. Gross domestic
product (GDP) grew at an annual average of 6.6%
from 1963 to 1973. Agricultural production grew
by 4.7% annually during the same period,
stimulated by redistributing estates, diffusing
new crop strains, and opening new areas to
cultivation. After experiencing moderately high
growth rates during the 1960s and 1970s, Kenya's
economic performance during the 1980s and 1990s
was far below its potential. The economy grew by
an annual average of only 1.5% between 1997 and
2002, which was below the population growth
estimated at 2.5% per annum, leading to a
decline in per capita incomes. The decline in
economic performance in the last two decades was
largely due to inappropriate agricultural
policies, inadequate credit, and poor
international terms of trade contributing to the
decline in agriculture. Kenya's inward-looking
policy of import substitution and rising oil
prices made Kenya's manufacturing sector
uncompetitive. The government began a massive
intrusion in the private sector. Lack of export
incentives, tight import controls, and foreign
exchange controls made the domestic environment
for investment even less attractive.
From 1991 to 1993, Kenya had its worst economic
performance since independence. Growth in GDP
stagnated, and agricultural production shrank at
an annual rate of 3.9%. Inflation reached a
record 100% in August 1993, and the government's
budget deficit was over 10% of GDP. As a result
of these combined problems, bilateral and
multilateral donors suspended program aid to
Kenya in 1991. In the 1990s, the government
implemented economic reform measures to
stabilize the economy and restore sustainable
growth. In 1994, nearly all administrative
controls on producer and retail prices, imports,
foreign exchange and grain marketing were
removed. The Government of Kenya privatized a
range of publicly owned companies, reduced the
number of civil servants, and introduced
conservative fiscal and monetary policies. By
the mid-1990s, the government lifted price
controls on petroleum products. In 1995,
foreigners were allowed to invest in the Nairobi
Stock Exchange (NSE). In July 1997, the
Government of Kenya refused to meet commitments
made earlier to the International Monetary Fund
(IMF) on governance reforms. As a result, the
IMF suspended lending for 3 years, and the World
Bank also put a $90-million structural
adjustment credit on hold.
The Government of Kenya took some positive steps
on reform, including the establishment of the
Kenyan Anti-Corruption Authority in 1999, and
the adoption of measures to improve the
transparency of government procurements and
reduce the government payroll. In July 2000, the
IMF signed a $150 million Poverty Reduction and
Growth Facility (PRGF), and the World Bank
followed suit shortly after with a $157 million
Economic and Public Sector Reform credit. The
Anti-Corruption Authority was declared
unconstitutional in December 2000, and other
parts of the reform effort faltered in 2001. The
IMF and World Bank again suspended their
programs.
Net foreign direct investment (FDI) was negative
from 2000-2003, but started trickling back in
2004, as demonstrated by an increase in the
number of enterprises operating in Export
Processing Zones (EPZs) from 66 to 74 between
2003 and 2004. The value of total investments
increased from Ksh18.7 billion (U.S. $247.3
million) in 2005 to Ksh20.1 billion (over U.S.
$278.3 million) in 2006. Following the end of
the Multifiber Arrangement (MFA) textile
agreement in January 2005, several textile and
apparel factories closed, leaving 68 EPZ
enterprises. In 2006, this number increased to
70 EPZ enterprises. According to the World
Bank's Migrations and Remittances Factbook 2008,
remittances rose from U.S. $338.3 million in
2004 to U.S. $1.3 billion in 2007, equivalent to
5.3% of the GDP.
The economy began to recover after 2002,
registering 2.8% growth in 2003, 4.3% in 2004,
5.8% in 2005, 6.1% in 2006, and 7.0% in 2007.
However, the violence that broke out after the
December 27, 2007 general election paralyzed the
economy in January and early February 2008 and
closed the Northern Corridor in Rift Valley
province, cutting off vital shipments of fuel
and other goods to Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi,
eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo and
South Sudan. Tourists fled, and agricultural
production in the breadbasket Rift Valley region
was crippled. The manufacturing sector had to
cut back operations by 70%, as unsafe roads
prevented movement of workers, inputs, or
products, and congestion at the Port of Mombasa
slowed imports and exports. The signing of a
reconciliation agreement on February 28 put the
economy back on track, but the damage in the
first quarter to agriculture, tourism,
consumption, investment, and the financial,
transport, and construction sectors is expected
to shave 2008 economic growth from the 8%
forecast to the 4%-6% level. Governments in
major source countries for tourists to Kenya
have lifted their travel advisories, and the
Kenyan Government and tourism industry will make
strenuous efforts to bring tourists back, but
revenues will be a small fraction of the
approximately $1 billion earned in 2007.
During President Kibaki's first term in office
(2003-2007), the Government of Kenya began an
ambitious economic reform program and resumed
its cooperation with the World Bank and the IMF.
The National Rainbow Coalition (NARC) government
enacted the Anti-Corruption and Economic Crimes
Act and Public Officers Ethics Act in May 2003
aimed at fighting graft in public offices. There
was some movement to reduce corruption in 2003,
but the government did not sustain that
momentum. Other reforms, especially in the
judiciary, public procurement, etc., led to the
unlocking of donor aid and a renewed hope of
economic revival.
In November 2003, following the signing into law
of key anti-corruption legislation and other
reforms by the Kibaki government, donors
reengaged as the IMF approved a three-year $250
million Poverty Reduction and Growth Facility
(PRGF) and donors committed $4.2 billion in
support over 4 years. In December 2004, the IMF
approved Kenya's Poverty Reduction and Growth
Facility arrangement equivalent to U.S. $252.8
million to support the government's economic and
governance reforms. However, the government's
ability to stimulate economic demand through
fiscal and monetary policy remains fairly
limited, while the pace at which the government
is pursuing reforms in other key areas remains
slow. The Privatization Law was enacted in 2005,
but only became operational as of January 1,
2008. Parastatals Kenya Electricity Generating
Company (KenGen), Kenya Railways, Telkom Kenya,
and Kenya Re-Insurance have been privatized, and
the government sold 25% of Safaricom (10 billion
shares) in 2008, reducing its share to 35%.
Accelerating growth to achieve Kenya's potential
and reduce the poverty that afflicts about 46%
of its population will require continued
de-regulation of business, improved delivery of
government services, addressing structural
reforms, massive investment in new
infrastructure (especially roads), reduction of
chronic insecurity caused by crime, and improved
economic governance generally. The government's
Vision 2030 plan calls for these reforms, but
implementation will be delayed by the
reconstruction effort, coalition politics, and
line ministries' limited capacity. In June 2008,
the government introduced a revised but still
ambitious Vision 2030 plan that seeks to address
the economic challenges stemming from the
political crisis while still striving to meet
growth benchmarks.
Economic expansion is fairly broad-based and is
built on a stable macro-environment fostered by
government, and the resilience, resourcefulness,
and improved confidence of the private sector.
Despite the post-election crisis, Nairobi
continues to be the primary communication and
financial hub of East Africa. It enjoys the
region's best transportation linkages,
communications infrastructure, and trained
personnel, although these advantages are less
prominent than in past years. On January 31,
2007, the government signed a $2.7 million
contract with Tyco Telecommunications to perform
an undersea survey for the construction of a
fiber-optic cable to Fujairah in the United Arab
Emirates (U.A.E.) called the East African Marine
Systems (TEAMS). Two other fiber-optic cables
projects are being pursued to link Kenya to the
rest of East Africa and India. Once TEAMS and
the domestic fiber-optic cables planned by the
government are completed, the economy is
expected to benefit significantly from reduced
internet access prices and improved capacity. A
wide range of foreign firms maintain regional
branches or representative offices in the city.
In March 1996, the Presidents of Kenya,
Tanzania, and Uganda re-established the East
African Community (EAC). The EAC's objectives
include harmonizing tariffs and customs regimes,
free movement of people, and improving regional
infrastructures. In March 2004, the three East
African countries signed a Customs Union
Agreement paving the way for a common market.
The Customs Union and a Common External Tariff
were established on January 1, 2005, but the EAC
countries are still working out exceptions to
the tariff. Rwanda and Burundi joined the
community in July 2007. In May 2007, during a
Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa
(COMESA) Summit, 13 heads of state endorsed a
move to adopt a COMESA customs union and set
December 8, 2008 as the target date for its
adoption.
In 2007, horticulture exports rose 65% to U.S.
$1.12 billion, surpassing tourism as the largest
foreign exchange earner. Tourism earned Kenya
U.S. $972 million in 2007, up from U.S. $803
million in 2006, followed by tea exports of U.S.
$638.9 million. Africa is Kenya's largest export
market, followed by the European Union (EU).
Kenya benefits significantly from the African
Growth and Opportunity Act (AGOA), but the
apparel industry is struggling to hold its
ground against Asian competition. Ninety-eight
percent of AGOA exports are garments, and
Kenya's AGOA exports fell from U.S. $265 million
in 2006 to U.S. $250 million in 2007.
Kenya faces profound environmental challenges
brought on by high population growth,
deforestation, shifting climate patterns, and
the overgrazing of cattle in marginal areas in
the north and west of the country. Significant
portions of the population will continue to
require emergency food assistance in the coming
years.
Media
The key independent print media in Kenya are
the Nation Media Group, the Standard Group,
People Limited, and the Times Media Group. The
Nation Media Group publications, which include
the Daily Nation, the Sunday Nation, the
Business Daily, the weekly East African, and the
only Swahili publications, Taifa Leo and Taifa
Jumapili, have the largest circulations. The
Standard and the Sunday Standard, published by
the Standard Group, are also popular newspapers,
although with smaller circulations.
Approximately 120 foreign correspondents
representing 100 media organizations report from
Nairobi. There is no government-owned or
controlled newspaper.
Major independent radio and television media are
the Kenya Television Network (KTN), the
broadcast media arm of the Standard Group;
Nation Radio/TV, owned by the Nation Media
Group; and Citizen Radio/Television, owned by
Royal Media Services. The government owns and
controls the Kenya Broadcasting Corporation (KBC)
and its subsidiaries. KBC is the only national
radio and television network.
Kenya also has hundreds of FM radio stations,
some broadcasting in Swahili or in local
languages. Radio has a wide reach in Kenya,
especially in rural areas. Some major
international broadcasters, including British
Broadcasting Corporation (BBC), Voice of America
(VOA) and Radio France Internationale (RFI),
rebroadcast their programming in Kenya.
FOREIGN RELATIONS
Despite internal tensions in Sudan and Ethiopia,
Kenya has maintained good relations with its
northern neighbors. Recent relations with Uganda
and Tanzania have improved as the three
countries work for mutual economic benefit.
Kenya has hosted and played an active role in
the negotiations to resolve the civil war in
Sudan and to reinstate a central government
authority in Somalia. The Sudan peace
negotiations have made major progress, resulting
in the signing in Kenya of agreements between
the Khartoum Government and the southern Sudan
rebels to put an end to the two-decade-long war.
On January 9, 2005 a Sudan North-South
Comprehensive Peace Accord was signed in
Nairobi. Negotiations in the Somali National
Reconciliation Conference resulted at the end of
2004 in the establishing of Somali Transitional
Federal Institutions (Assembly, President, Prime
Minister, and Government). Until early 2005,
Kenya served as a major host both for these
institutions and for refugees from Somalia as
well as Sudan. Between May and June 2005,
members of the Somalia Transitional Federal
Institutions relocated to Somalia.
Kenya maintains a moderate profile in Third
World politics. Kenya's relations with Western
countries are generally friendly, although
current political and economic instabilities are
sometimes blamed on Western pressures.
U.S.-KENYAN RELATIONS
The United States and Kenya have enjoyed cordial
relations since Kenya's independence. Relations
became even closer after Kenya's democratic
transition of 2002 and subsequent improvements
in human rights.
More than 9,000 U.S. citizens are registered
with the U.S. Embassy as residents of Kenya. In
2007 almost 100,000 Americans visited Kenya, up
18% from 2006. About two-thirds of resident
Americans are missionaries and their families.
U.S. business investment is estimated to be more
than $285 million, primarily in commerce, light
manufacturing, and the tourism industry.
Al Qaeda terrorists bombed the U.S. Embassy in
Nairobi on August 7, 1998, taking hundreds of
lives and maiming thousands more. Since that
event, the Kenyan and U.S. Governments have
intensified cooperation to address all forms of
insecurity in Kenya, including terrorism. The
United States provides equipment and training to
Kenyan security forces, both civilian and
military. In its dialog with the Kenyan
Government, the United States urges effective
action against corruption and insecurity as the
two greatest impediments to Kenya achieving
sustained, rapid economic growth.
U.S. assistance to Kenya is substantial. It
promotes broad-based economic development as the
basis for continued progress in political,
social, and related areas of national life. The
U.S. assistance strategy is built around five
broad objectives: Fighting disease and improving
healthcare; fighting poverty and promoting
private sector-led prosperity; advancing shared
democratic values, human rights, and good
governance; cooperating to fight insecurity and
terrorism; and collaborating to foster peace and
stability in East Africa. The Peace Corps, which
usually has 150 volunteers in Kenya, is integral
to the overall U.S. assistance strategy in
Kenya. Peace Corps volunteers were withdrawn
from Kenya due to instability and civil unrest
in early 2008, but the program resumed Kenya
operations within a few months.
Principal U.S. Officials
Ambassador--Michael
E. Ranneberger
Deputy Chief of Mission--Pamela Slutz
USAID Mission Director--Erna Kerst
Public Affairs Officer--T.J. Dowling
The U.S.
Embassy in
Kenya is located on UN Avenue, Nairobi, P.O. Box
606, Village Market, Nairobi (tel.
254-20-363-6000; fax 254-20-363-6157).
 Information
on Countries from Around the World
Information
on Countries from Around the World Information
on Countries from Around the World
Information
on Countries from Around the World