
PROFILE
OFFICIAL NAME:
Republic of Niger
Geography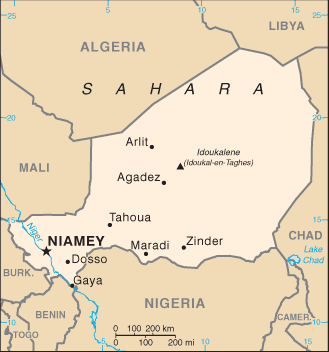
Area: 1,267,000 sq. km (490,000 sq. mi.); about
three times the size of California.
Cities: Capital--Niamey
(pop. approx. 1 million).
Other cities--Tahoua, Konni, Maradi,
Zinder, Diffa, Dosso, Arlit, and Agadez.
Terrain: About two-thirds desert and mountains,
one-third savanna.
Climate: Hot, dry, and dusty. Rainy season June
- September.
People
Nationality: Noun
and Adjective--Nigerien(s).
Population (2007 est.) 14,853,000.
Annual growth rate (2005): 3.3%.
Ethnic groups: Hausa 53%, Djerma (Zarma) 21%,
Fulani 7%, Tuareg 11%, Beri Beri (Kanuri) 6%;
Arab, Toubou, and Gourmantche 2%.
Religions: Islam (99%); remainder traditional
and Christian.
Languages: French (official), Hausa, Djerma,
Fulfulde, Kanuri, Tamachek, Toubou, Gourmantche,
Arabic.
Education: Years
compulsory--6. Attendance--45%
(men), 31% (women). Literacy (2005)--28.7%
(15% for women).
Health: Infant
mortality rate--150/1,000. Life
expectancy--54.5 yrs.
Government
Type: Republic.
Independence: August 3, 1960.
Constitution: The constitution of December 26,
1992 was revised by national referendum on May
12, 1996 and again by referendum on July 18,
1999.
Branches: Executive--president
and prime minister. Legislative--unicameral
National Assembly (113 MPs). Judicial--Constitutional
Court, Supreme Court, Court of Appeals, High
Court of Justice.
Political parties: Seven are represented in the
National Assembly.
Suffrage: The constitution provides for
universal suffrage for Nigeriens age 18 or
older.
Administrative subdivisions: Eight regions
subdivided into 36 districts (departments) and
265 communes (local councils).
Economy
GDP (2006): $3.54 billion.
Annual growth rate (2006): 4.8%.
Per capita GDP (2006): $273.
Avg. inflation rate (2006): 0.1%.
Natural resources: Uranium, gold, oil, coal,
iron, tin, and phosphates.
Agriculture (27.9% of GDP): Products--millet,
sorghum, cowpeas, peanuts, cotton, and rice.
Industry (10.5% of GDP): Types--textiles,
cement, soap, and beverages.
Trade (2006): Exports (freight
on board--f.o.b.)--$275 million. Types--uranium,
livestock, gold, cowpeas, and onions. Major
markets--France 34.8%, Nigeria 16.7%, Japan
13.3%, Spain 9.5%, U.S. 0.3%. Imports
(f.o.b.)--$792 million. Types--consumer
goods, petroleum, foodstuffs, and industrial
products. Major
suppliers--France 16.3%, China 13.1%, U.S.
7.1%, Nigeria 6.6%, Cote d'Ivoire 6.3%, India
4.7%, Japan 3.9%.
PEOPLE
The largest ethnic groups in Niger are the
Hausa, who also constitute the major ethnic
group in northern Nigeria, and the Djerma-Songhai,
who also are found in parts of Mali. Both
groups, along with the Gourmantche, are
sedentary farmers who live in the arable,
southern tier of the country. The remainder of
Nigeriens are nomadic or semi-nomadic
livestock-raising peoples--Fulani, Tuareg,
Kanuri, Arabs, and Toubou. With rapidly growing
populations and the consequent competition for
meager natural resources, lifestyles of
agriculturalists and livestock herders are
increasingly threatened.
Niger's high infant mortality rate is comparable
to levels recorded in neighboring countries.
However, the child mortality rate (deaths among
children under age of 5) is particularly high
(198 per 1,000) due to generally poor health
conditions and inadequate nutrition for most of
the country's children. Nonetheless, Niger's
fertility rate (7.8 births/woman), is among the
highest in the world, and is far higher than the
sub-Saharan African average of 5.4. Two-thirds
(66.7%) of the Nigerien population is under age
25. Primary school net enrollment rate is 49%
for boys and 31% for girls. Additional education
occurs through thousands of Koranic schools.
HISTORY
Considerable evidence indicates that about
600,000 years ago, humans inhabited what has
since become the desolate Sahara of northern
Niger. Long before the arrival of French
influence and control in the area, Niger was an
important economic crossroads, and the empires
of Songhai, Mali, Gao, Kanem, and Bornu, as well
as a number of Hausa states, claimed control
over portions of the area.
During recent centuries, the nomadic Tuareg
formed large confederations, pushed southward,
and, siding with various Hausa states, clashed
with the Fulani Empire of Sokoto, which had
gained control of much of the Hausa territory in
the late 18th century.
In the 19th century, contact with the West began
when the first European explorers--notably Mungo
Park (British) and Heinrich Barth
(German)--explored the area searching for the
mouth of the Niger River. Although French
efforts at pacification began before 1900,
dissident ethnic groups, especially the desert
Tuareg, were not subdued until 1922, when Niger
became a French colony.
Niger's colonial history and development
parallel that of other French West African
territories. France administered its West
African colonies through a governor general at
Dakar, Senegal, and governors in the individual
territories, including Niger. In addition to
conferring French citizenship on the inhabitants
of the territories, the 1946 French constitution
provided for decentralization of power and
limited participation in political life for
local advisory assemblies.
A further revision in the organization of
overseas territories occurred with the passage
of the Overseas Reform Act (Loi Cadre) of July
23, 1956, followed by reorganization measures
enacted by the French Parliament early in 1957.
In addition to removing voting inequalities,
these laws provided for creation of governmental
organs, assuring individual territories a large
measure of self-government. After the
establishment of the Fifth French Republic on
December 4, 1958, Niger became an autonomous
state within the French Community. Following
full independence on August 3, 1960, however,
membership was allowed to lapse.
For its first 14 years as an independent state,
Niger was run by a single-party civilian regime
under the presidency of Hamani Diori. In 1974, a
combination of devastating drought and
accusations of rampant corruption resulted in a
military coup that overthrew the Diori regime.
Lieutenant Colonel Seyni Kountche and a small
group of military ruled the country until
Kountche's death in 1987. He was succeeded by
his Chief of Staff, Brigadier General Ali Saibou,
who released political prisoners, liberalized
some of Niger's laws and policies, and
promulgated a new constitution. However,
President Saibou's efforts to control political
reforms failed in the face of union and student
demands to institute a multi-party democratic
system. The Saibou regime acquiesced to these
demands by the end of 1990. New political
parties and civic associations sprang up, and a
national conference was convened in July 1991 to
prepare the way for the adoption of a new
constitution and the holding of free and fair
elections. The debate was often contentious and
accusatory, but under the leadership of Prof.
Andre Salifou, the conference developed
consensus on the modalities of a transition
government. A transition government was
installed in November 1991 to manage the affairs
of state until the institutions of the Third
Republic were put into place in April 1993.
While the economy deteriorated over the course
of the transition, certain accomplishments stand
out, including the successful conduct of a
constitutional referendum; the adoption of key
legislation such as the electoral and rural
codes; and the holding of several free, fair,
and nonviolent nationwide elections. Freedom of
the press flourished with the appearance of
several new independent newspapers.
Rivalries within a ruling coalition elected in
1993 led to governmental paralysis, which
provided Col. Ibrahim Baré Maïnassara a
rationale to overthrow the Third Republic and
its President, Mahamane Ousmane, in January
1996. While leading a military authority that
ran the government (Conseil de Salut National)
during a 6-month transition period, Bare
enlisted specialists to draft a new constitution
for a Fourth Republic announced in May 1996.
After dissolving the national electoral
committee, Bare organized and won a flawed
presidential election in July 1996 and his party
won 90% of parliament seats in a flawed
legislative election in November 1996. When his
efforts to justify his coup and subsequent
questionable elections failed to convince donors
to restore multilateral and bilateral economic
assistance, a desperate Bare ignored an
international embargo against Libya and sought
Libyan funds to aid Niger's economy. In repeated
violations of basic civil liberties by the
regime, opposition leaders were imprisoned;
journalists often arrested, beaten, and deported
by an unofficial militia composed of police and
military; and independent media offices were
looted and burned with impunity.
In the culmination of an initiative started
under the 1991 national conference, however, the
government signed peace accords in April 1995
with all Tuareg and Toubou groups that had been
in rebellion since 1990, claiming they lacked
attention and resources from the central
government. The government agreed to absorb some
former rebels into the military and, with French
assistance, help others return to a productive
civilian life.
In April 1999, Bare was overthrown and
assassinated in a coup led by Maj. Daouda Mallam
Wanke, who established a transitional National
Reconciliation Council to oversee the drafting
of a constitution for a Fifth Republic with a
French style semi-presidential system. In votes
that international observers found to be
generally free and fair, the Nigerien electorate
approved the new constitution in July 1999 and
held legislative and presidential elections in
October and November 1999. Heading a coalition
of the National Movement for a Developing
Society (MNSD) and the Democratic and Social
Convention (CDS), Mamadou Tandja won the
presidency.
In July 2004, Niger held municipal elections
nationwide as part of its decentralization
process. Some 3,700 people were elected to new
local governments in 265 newly established
communes. The ruling MNSD party won more
positions than any other political party;
however, opposition parties made significant
gains.
In November and December 2004, Niger held
presidential and legislative elections. Mamadou
Tandja was elected to his second 5-year
presidential term with 65% of the vote in an
election that international observers called
generally free and fair. This was the first
presidential election with a democratically
elected incumbent and a test to Niger's young
democracy.
In the 2004 legislative elections, the National
Movement for the Development of Society (MNSD),
the Democratic and Socialist Convention (CDS),
the Rally for Social Democracy (RSD), the Rally
for Democracy and Progress (RDP), the Nigerien
Alliance for Democracy and Progress (ANDP), and
the Social Party for Nigerien Democracy (PSDN)
coalition, which backed Tandja, won 88 of the
113 seats in the National Assembly.
A previously unknown group, the Mouvement des
Nigeriens pour la Justice (MNJ), emerged in
February 2007. The predominantly Tuareg group
has issued a number of demands, mainly related
to development in the north. It has attacked
military and other facilities and laid landmines
in the north. The resulting insecurity has
devastated Niger's tourist industry and deterred
investment in mining and oil. The government has
labeled the MNJ criminals and traffickers, and
refuses to negotiate with the group until it
disarms.
GOVERNMENT AND POLITICAL CONDITIONS
Niger's new constitution was approved in July
1999. It restored the semi-presidential system
of government of the December 1992 constitution
(Third Republic) in which the president of the
republic, elected by universal suffrage for a
5-year term, and a prime minister named by the
president share executive power. As a reflection
of Niger's increasing population, the unicameral
legislature was expanded in 2004 to 113 deputies
elected for a 5-year term under a proportional
system of representation. Political parties must
attain at least 5% of the vote in order to gain
a seat in the legislature.
Niger's independent judicial system is composed
of four higher courts--the Court of Appeals, the
Supreme Court, the High Court of Justice, and
the Constitutional Court. In January 2007, the
National Assembly voted to divide the Supreme
Court into three high courts--an Administrative
Court, a Supreme Court of Justice, and an Audit
Court.
The constitution also provides for the popular
election of municipal and local officials, and
the first-ever successful municipal elections
took place July 24, 2004. The National Assembly
passed in June 2002 a series of decentralization
bills. As a first step, administrative powers
have been distributed among 265 communes (local
councils); in later stages, regions and
departments will be established as decentralized
entities. A new electoral code was adopted to
reflect the decentralization context. The
country is currently divided into 8 regions,
which are subdivided into 36 districts
(departments). The chief administrators in each
region (Governor) and department (Prefect) are
appointed by the government and function
primarily as the local agents of the central
authorities.
The current legislature elected in December 2004
contains seven political parties. President
Mamadou Tandja was re-elected in December 2004
and reappointed Hama Amadou as Prime Minister.
Mahamane Ousmane, the head of the CDS, was
re-elected President of the National Assembly
(parliament) by his peers. The new second term
government of the Fifth Republic took office on
December 30, 2004. In May 2007, Hama Amadou
stepped down as Prime Minister following a vote
of no confidence by the National Assembly
related to allegations of his involvement in a
corruption scandal, and President Tandja
appointed Seini Oumarou Prime Minister as head
of a new cabinet.
Principal Government Officials
President and Chief of State--Mamadou Tandja
Prime Minister--Seini Oumarou
Minister of Foreign Affairs and
Cooperation--Aïchatou Mindaoudou
Ambassador to the United States--Aminata Maiga
Djibrilla Toure
Niger maintains an embassy in
the United States at 2204 R Street, NW,
Washington, DC 20008 (tel.
202-483-4224/25/26/27) and a permanent mission
to the United Nations at 417 East 50th Street,
New York, NY 10022 (tel. 212-421-3260).
Next Elections Scheduled
Presidential elections--November/December
2009, two rounds; no date selected.
Legislative elections--December 2009; no date
selected.
Local elections--Not scheduled, but expected in
late 2008 or in 2009. Last local election was in
July 2004.
ECONOMY
One of the poorest countries in the world,
ranking last on the United Nations Human
Development Index, Niger's economy is based
largely on subsistence crops, livestock, and
some of the world's largest uranium deposits.
Traditional subsistence farming, herding, small
trading, seasonal migration, and informal
markets dominate an economy that generates few
formal sector jobs.
Niger's agricultural and livestock sectors are
the mainstay of all but 20% of the population.
Fourteen percent of Niger's GDP is generated by
livestock production--camels, goats, sheep, and
cattle--said to support 29% of the population.
The 15% of Niger's land that is arable is found
mainly along its southern border with Nigeria.
Rainfall varies and when insufficient, Niger has
difficulty feeding its population and must rely
on grain purchases and food aid to meet food
requirements. In 2004 localized drought and
locust infestations contributed to a drop in
global harvests of 11% and led the Embassy to
make a disaster declaration. This decrease,
combined with chronic structural food
insecurity, high malnutrition, and other market
factors, triggered a food crisis which began in
May-June of 2005. Although food security
continues to be a concern, the food crisis has
ended as a result of good cereal harvests in
2005, 2006, and 2007. Millet and sorghum are
Niger's principal rain-fed subsistence crops.
Cowpeas and onions are grown for commercial
export, as are limited quantities of garlic,
peppers, gum arabic, and sesame seeds.
In 2006, foreign exchange earnings from
livestock (14.7%) were second only to those from
uranium (55.4%), followed by gold (13.6%) and
agricultural products (9.9%). Actual livestock
exports far exceed official statistics, which
often fail to detect large herds of animals
informally crossing into Nigeria. Some hides and
skins are exported, and some are transformed
into handicrafts.
Recent global price increases have led to higher
revenues for Niger's uranium sector, which
provides approximately 55.4% of national export
proceeds. The nation enjoyed substantial export
earnings and rapid economic growth during the
1960s and 1970s; however, when the uranium-led
boom ended in the early 1980s the economy
stagnated. The French nuclear power concern
AREVA owns controlling shares in Niger's two
national mining companies. As a result of higher
world prices in 2007, AREVA agreed to pay the
Government of Niger double what it had been
paying for uranium. In 2007 the U.S. public
utility holding company Exelon Corporation
signed a contract with the Government of Niger
to buy 300 tons of uranium each year for the
next 10 years. Although AREVA controls the only
two existing uranium mines in Niger (COMINAK's
underground mine and SOMAIR's open pit mine), in
2007 the Government of Niger awarded 122 new
mineral exploration licenses to companies from
France, China, Canada, Australia, India, South
Africa, and the United States.
Exploitable deposits of gold are known to exist
in Niger in the region between the Niger River
and the border with Burkina Faso. On October 5,
2004 President Tandja announced the official
opening of the Samira Hill Gold Mine in the
region of Tera and the first Nigerien gold ingot
was presented to him. This marked a historical
moment for Niger as the Samira Hill Gold Mine
represents the first commercial gold production
in the country. Samira Hill is owned by a
company called SML (Societe des Mines du
Liptako), which is a joint venture between a
Moroccan company--Societe SEMAFO Inc.--and a
Canadian company--ETRUSCAN. Both companies own
80% (40% - 40%) of SML and the Government of
Niger 20%. In 2006, gold was Niger's third most
important export, accounting for 13.6% of the
country's total exports. In 2007 the
Anglo-American company Caracal Gold Burkina was
awarded two permits to explore for gold in the
Tillaberi region.
Niger has oil potential. In 2006 an
ExxonMobil-Petronas joint venture ceased
exploration activities at what may be Niger's
largest oil deposit, the Agadem block, located
north of Lake Chad. In 2007 nineteen companies
vied for exploration and production rights to
the Agadem block, but none of these bids were
accepted. The Government of Niger is expected to
award the Agadem block in 2008. The parastatal
SONICHAR (Societe Nigerienne de Charbon) in
Tchirozerine (north of Agadez) extracts coal
from an open pit and fuels an electricity
generating plant that supplies energy to the
uranium mines. There are additional coal
deposits southwest of the current mines.
Substantial deposits of phosphates, iron,
limestone, and gypsum also have been found in
Niger.
Niger enjoyed increased economic competitiveness
following the January 1994 devaluation of the
Communaute Financiere Africaine (CFA) franc.
Annual economic growth rates vary widely, due
largely to the effect of rainfall on
agricultural output. In 2005 the economy showed
strong growth (7.1% real GDP growth) as a result
of the agricultural sector's recovery from the
poor harvests of 2004, and the continued growth
of non-agricultural sectors. In 2006, the real
GDP growth rate was at 5.1%.
The government actively seeks foreign private
investment and considers it key to restoring
economic growth and development. With the
assistance of the United Nations Development
Program (UNDP), it has undertaken a concerted
effort to revitalize the private sector. It
revised the investment code (1997 and 2000),
petroleum code (1992 and 2007), and mining code
(1993) aimed at attracting investors.
Niger shares a common currency, the CFA franc,
and a common central bank, the Central Bank of
West African States (BCEAO), with seven other
members of the West African Monetary Union. The
Treasury of the Government of France supplements
the BCEAO's international reserves in order to
maintain a fixed rate of 656 CFA to the euro.
Economic Reform
In January 2000, Niger's newly elected
government inherited serious financial and
economic problems, including a virtually empty
treasury, past-due salaries (11 months of
arrears) and scholarship payments, increased
debt, reduced revenue performance, and lower
public investment. In December 2000, Niger
qualified for enhanced debt relief under the
International Monetary Fund (IMF) program for
Highly Indebted Poor Countries (HIPC) and
concluded an agreement with the Fund on a
Poverty Reduction and Growth Facility (PRGF). In
January 2001, Niger reached its decision point
and subsequently reached its completion point in
2004. The debt relief provided under the
enhanced HIPC initiative significantly reduces
Niger's annual debt service obligations, freeing
about $40 million per year over the coming years
for expenditures on basic health care, primary
education, HIV/AIDS prevention, rural
infrastructure, and other programs geared at
poverty reduction. Debt service as a percent of
government revenue was slashed from nearly 44%
in 1999 to 10.9% in 2003 and will average 4.3%
during 2010-2019. The debt relief cut debt
service as a percentage of export revenue from
more than 23% to 8.4% in 2003, and decreases it
to about 5% in later years. In 2005, the IMF
canceled all of Niger's debts to it
(approximately $111 million) incurred before
January 2005. In 2006, the African Development
Fund canceled $193 million in debt for Niger.
Furthermore, the World Bank announced that
approximately $745 million in debt relief for
Niger would be phased in over the next 37 years.
In its effort to consolidate macroeconomic
stability under the PRGF, the government is also
taking action to reduce corruption, and as the
result of a participatory process encompassing
civil society, has devised a Poverty Reduction
Strategy Plan that focuses on improving health,
primary education, rural infrastructure,
agricultural production, environmental
protection, and judicial reform. In late 2006,
Niger qualified for the Millennium Challenge
Corporation's (MCC) Threshold Program. Niger
will focus its MCC efforts on promoting girls'
education, fighting corruption, and improving
the business environment.
Under the auspices of the World Bank, the
government launched a major privatization effort
in 1998 to divest itself of monopolies in water,
power, and telecommunications and to transfer
other public enterprises to private sector
management. In 2001 Niger successfully
privatized its telecommunications monopoly;
however, the privatization of other industries
has stalled. The privatization of the
state-owned electric utility (NIGELEC) and the
national oil distribution company (SONIDEP) are
on hold indefinitely.
Foreign Aid
The most important donors in Niger are
France, the European Union, the World Bank, the
IMF, and UN agencies--UNDP, UNICEF, FAO, WFP,
and UNFPA. Other donors include the United
States, Belgium, Germany, Switzerland, Japan,
China, Italy, Libya, Egypt, Morocco, Iran,
Denmark, Canada, and Saudi Arabia. While the
U.S. Agency for International Development
(USAID) does not have a Mission in Niger, the
United States is a major donor, contributing on
average $30 million each year to Niger's
development. In early 2008 Niger concluded an
agreement for a $23 million Millennium Challenge
Account threshold program. Niger is a key
participant in the Trans-Saharan
Counter-Terrorism program. Niger also benefits
from the largest non-emergency PL 480 food
assistance program in West Africa. Foreign aid
represents 8.3% of Niger's GDP and over 40% of
government revenues.
DEFENSE
The Niger Armed Forces total 12,000
personnel with approximately 3,700 gendarmes,
300 air force, and 8,000 army personnel. The air
force has four transport aircraft. The armed
forces include general staff and battalion task
force organizations consisting of two paratroop
units, four light armored units, and nine
motorized infantry units located in Tahoua,
Agadez, Dirkou, Zinder, Nguigmi, N'Gourti, and
Madewela. In 1991, Niger sent a 400-man military
contingent to join the American-led allied
forces against Iraq during the Gulf War. Niger
provides a battalion of peace-keeping forces to
the UN Mission in Cote d'Ivoire.
Niger's defense budget is modest, accounting for
about 1.6% of government expenditures. France
provides the largest share of military
assistance to Niger. Approximately 18 French
military advisers are in Niger. Many Nigerien
military personnel receive training in France,
and the Nigerien Armed Forces are equipped
mainly with materiel either given by or
purchased in France. Morocco, Algeria, China,
and Libya are also providing military
assistance. A small U.S. foreign military
assistance program was initiated in 1983. A U.S.
Defense Attaché office opened in June 1985 and
assumed Security Assistance Office
responsibilities in 1987. The office closed in
1996 following a coup d'état. The U.S. Defense
Attaché office reopened in July 2000. The United
States provided transportation and logistical
assistance to Nigerien troops deployed to Cote
d'Ivoire in 2003.
Additionally, the U.S. provided initial
equipment training on vehicles and
communications gear to a company of Nigerien
soldiers as part of the Department of State
Pan-Sahel Initiative. Military to military
cooperation continues via the Trans Saharan
Counter-Terrorism Partnership and other
initiatives. EUCOM contributes funds for
humanitarian assistance construction throughout
the country. In 2007, a congressional waiver was
granted which allows the Niger military to
participate in the International Military
Education and Training (IMET) program, managed
by the Defense Attache Office. This program
funded $170,000 in training in 2007.
FOREIGN RELATIONS
Niger pursues a moderate foreign policy and
maintains friendly relations with the West and
the Islamic world as well as nonaligned
countries. It belongs to the United Nations and
its main specialized agencies and in 1980-81
served on the UN Security Council. Niger
maintains a special relationship with France and
enjoys close relations with its West African
neighbors. It is a charter member of the African
Union and the West African Monetary Union and
also belongs to the Niger River and Lake Chad
Basin Commissions, the Economic Community of
West African States, the Nonaligned Movement,
and the Organization of the Islamic Conference.
U.S.-NIGERIEN RELATIONS
U.S. relations with Niger have generally
been close and friendly since Niger attained
independence. Although USAID does not have a
Mission in Niger, $30 million in annual official
aid is administered through American and local
non-governmental organizations with programs
addressing food security, health, local
governance, youth training, girls' education,
corruption control, and improving the business
environment. The U.S.
Peace Corps program
in Niger started in 1962. It currently has about
130 volunteers in country and celebrated its
45th anniversary in Niger in September 2007.
Principal U.S. Officials
Ambassador--Bernadette
M. Allen
Deputy Chief of Mission--Eric Whitaker
Defense Attaché--vacant
Joint Management Officer--Sonja Rix
Economic/Commercial/Consular Officer--Karen
Swaner
Public Affairs Officer--Stephen J. Posivak
Peace Corps Director--Mary Abrams
USAID Country Program Manager--Mark Wentling
The U.S.
Embassy in
Niger is located on the Avenue des Ambassades.
The telephone numbers for the embassy are (227)
20-72-26-61 through 65, and the fax number is
(227) 20-73-31-67. The mailing address is B.P.
11201, Niamey.
 Information
on Countries from Around the World
Information
on Countries from Around the World Information
on Countries from Around the World
Information
on Countries from Around the World