
PROFILE
OFFICIAL NAME:
Somalia
Geography
Area: 637,657 sq. km.; slightly smaller than
Texas.
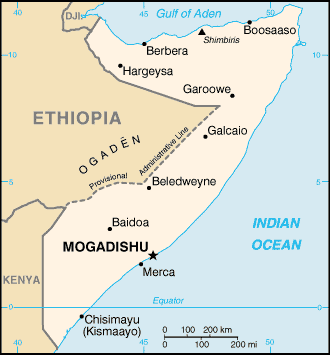
Cities: Capital--Mogadishu. Other
cities--Beledweyne, Kismayo, Baidoa, Jowhar,
Merca, Gaalkayo, Bosasso, Hargeisa, Berbera.
Terrain: Mostly flat to undulating plateau
rising to hills in the north.
Climate: Principally desert; December to
February--northeast monsoon, moderate
temperatures in north, and very hot in the
south; May to October--southwest monsoon, torrid
in the north, and hot in the south; irregular
rainfall; hot and humid periods (tangambili)
between monsoons.
People
Nationality: Noun--Somali(s). Adjective--Somali.
Population (2006 est., no census exists): 8.8
million (of which an estimated 2 million in
Somaliland).
Annual growth rate (2006 est.): 2.85%.
Ethnic groups: Somali, with a small non-Somali
minority (mostly Bantu and Arabs).
Religion: 99.9% Muslim.
Languages: Somali (official), Arabic, Italian,
English.
Education: Literacy--total
population that can read and write, 37.8%: male
49.7%; female 25.8%.
Health: Infant
mortality rate--114.9/1,000 live births. Life
expectancy at birth--total population: 48.7
yrs.
Work force (3.7 million; very few are skilled
workers): Pastoral
nomad--60%. Agriculture, government,
trading, fishing, industry, handicrafts, and
other--40%.
Government
Type: Transitional government, known as the
Transitional Federal Government, established in
October 2004 with a 5-year mandate leading to
the establishment of a permanent government
following national elections in 2009.
Independence: July 1, 1960 (from a merger
between the former Somaliland Protectorate under
British rule, which became independent from the
U.K. on June 26, 1960, and Italian Somaliland,
which became independent from the
Italian-administered UN trusteeship on July 1,
1960, to form the Somali Republic).
Constitution: None in force. Note: A
Transitional Federal Charter was established in
February 2004 and is expected to serve as the
basis for a future constitution in Somalia. In
August 2004, the Somali Transitional Federal
Assembly (TFA) was established as part of the
IGAD-led Somalia National Reconciliation
Conference in accordance with the Charter. The
Somalia National Reconciliation Conference
concluded following the election of a
Transitional President in October 2004.
Branches: Executive--On
October 10, 2004, Abdullahi Yusuf Ahmed was
elected Transitional Federal President of
Somalia for a five-year period. On October 29,
2007, Ali Mohamed Gedi resigned as Prime
Minister of the Transitional Federal Government.
On November 22, 2007, President Yusuf appointed
Nur "Adde" Hassan Hussein as the new Prime
Minister of the Transitional Federal Government.
A cabinet, known as the Council of Ministers,
also exists. Legislative--parliamentary:
Transitional Federal Assembly, established in
August 2004. Sheikh Adan Mohamed Nur was elected
Speaker of the Assembly on January 31, 2007. Judicial--Supreme
Court not functioning; no functioning nationwide
legal system; informal legal system based on
previously codified law, Islamic (shari'a) law,
customary practices, and the provisions of the
Transitional Federal Charter.
Political party: None.
Note: In 1991, a congress drawn from the
inhabitants of the former Somaliland
Protectorate declared withdrawal from the 1960
union with Somalia to form the self-declared
Republic of Somaliland. Somaliland has not
received international recognition, but has
maintained a de jure separate status since that
time. Its form of government is republican, with
a bicameral legislature including an elected
elders chamber and a house of representatives.
The judiciary is independent, and various
political parties exist. In line with the
Somaliland Constitution, Vice President Dahir
Riyale Kahin assumed the presidency following
the death of former president Mohamed Ibrahim
Egal in 2002. Kahin was elected President of
Somaliland in elections determined to be free
and fair by international observers in May 2003.
Elections for the 84-member lower house of
parliament took place on September 29, 2005 and
were described as transparent and credible by
international observers.
Suffrage: 18 years of age; universal (no
nationwide elections).
Administrative subdivisions: 18 regions (plural--NA; singular--Gobolka).
Awdal, Bakool, Banaadir, Bari, Bay, Galguduud,
Gedo, Hiraan, Jubbada Dhexe, Jubbada Hoose,
Mudug, Nugaal, Sanaag, Shabeellaha Dhexe,
Shabeellah Hoose, Sool, Togdheer, Woqooyi
Galbeed.
Central government budget: N/A.
Defense: N/A.
National holiday: July 1 (June 26 in
Somaliland).
Economy
GDP (2005 est.): U.S. $4.809 billion.
Annual growth rate (2005 est.): 2.4%.
Per capita GDP (2005 est.): $600.
Avg. inflation rate: N/A.
Natural resources: Largely unexploited reserves
of iron ore, tin, gypsum, bauxite, uranium,
copper, and salt; likely petroleum and natural
gas reserves.
Agriculture: Products--livestock,
fish, bananas, corn, sorghum, sugar. Arable
land--13%, of which 2% is cultivated.
Industry: Types--Telecommunications,
livestock, fishing, textiles, transportation,
and limited financial services. Somalia's
surprisingly innovative private sector has
continued to function despite the lack of a
functioning central government since 1991.
Trade: Exports--$241
million (f.o.b., 2004 est.): livestock, bananas,
hides, fish, charcoal, scrap metal. Major
markets--United Arab Emirates, Yemen, Oman. Imports--$576
million (f.o.b., 2004 est.): food grains, animal
and vegetable oils, petroleum products,
construction materials, manufactured products,
qat. Major
suppliers--Djibouti, Kenya, Brazil, India,
United Arab Emirates, Oman.
Aid disbursed: N/A. Primary donors--United
States, European Union, Australia, Canada,
Denmark, France, Germany, Italy, Japan,
Netherlands, Norway, Sweden, Switzerland, United
Kingdom.
Remittances (2006 est.): $800 million to $1
billion.
GEOGRAPHY
Somalia is located on the east coast of
Africa on and north of the Equator and, with
Ethiopia, Eritrea, Djibouti, and Kenya, is often
referred to as the Horn of Africa. It comprises
Italy's former Trust Territory of Somalia and
the former British Protectorate of Somaliland
(now seeking recognition as an independent
state). The coastline extends 2,720 kilometers
(1,700 mi.).
The northern part of the country is hilly, and
in many places the altitude ranges between 900
and 2,100 meters (3,000 ft.-7,000 ft.) above sea
level. The central and southern areas are flat,
with an average altitude of less than 180 meters
(600 ft.). The Juba and the Shabelle Rivers rise
in Ethiopia and flow south across the country
toward the Indian Ocean. The Shabelle, however,
does not reach the sea.
Major climatic factors are a year-round hot
climate, seasonal monsoon winds, and irregular
rainfall with recurring droughts. Mean daily
maximum temperatures range from 30oC
to 40oC (85o F-105oF),
except at higher elevations and along the east
coast. Mean daily minimums usually vary from
about 15oC to 30oC (60oF-85oF).
The southwest monsoon, a sea breeze, makes the
period from about May to October the mildest
season in Somalia. The December-February period
of the northeast monsoon also is relatively
mild, although prevailing climatic conditions in
Somalia are rarely pleasant. The "tangambili"
periods that intervene between the two rainy
seasons (October-November and March-May) are hot
and humid.
PEOPLE
The Cushitic populations of the Somali Coast in
the Horn of Africa have an ancient history.
Known by ancient Arabs as the Berberi,
archaeological evidence indicates their presence
in the Horn of Africa by A.D. 100 and possibly
earlier. As early as the seventh century A.D.,
the indigenous Cushitic peoples began to mingle
with Arab and Persian traders who had settled
along the coast. Interaction over the centuries
led to the emergence of a Somali culture bound
by common traditions, a single language, and the
Islamic faith.
The Somali-populated region of the Horn of
Africa stretches from the Gulf of Tadjoura in
modern-day Djibouti through Dire Dawa, Ethiopia,
and down to the coastal regions of southern
Kenya. Unlike many countries in Africa, the
Somali nation extends beyond its national
borders. Since gaining independence in 1960, the
goal of Somali nationalism, also known as Pan-Somalism,
has been the unification of all Somali
populations, forming a Greater Somalia. This
issue has been a major cause of past crises
between Somalia and its neighbors--Ethiopia,
Kenya, and Djibouti.
Today, about 60% of all Somalis are nomadic or
semi-nomadic pastoralists who raise cattle,
camels, sheep, and goats. About 25% of the
population is settled farmers who live mainly in
the fertile agricultural zone between the Juba
and Shabelle Rivers in southern Somalia. The
remainder of the population (15%-20%) is urban.
Sizable ethnic groups in the country include
Bantu agricultural workers, several thousand
Arabs and some hundreds of Indians and
Pakistanis. Nearly all inhabitants speak the
Somali language, which remained unwritten until
October 1973, when the Supreme Revolutionary
Council (SRC) proclaimed it the nation's
official language and decreed an orthography
using Latin letters. Somali is now the language
of instruction in schools, although Arabic,
English, and Italian also are used extensively.
HISTORY
Early history traces the development of the
Somali state to an Arab sultanate, which was
founded in the seventh century A.D. by
Koreishite immigrants from Yemen. During the
15th and 16th centuries, Portuguese traders
landed in present Somali territory and ruled
several coastal towns. The sultan of Oman and
Zanzibar subsequently took control of these
towns and their surrounding territory.
Somalia's modern history began in the late 19th
century, when various European powers began to
trade and establish themselves in the area. The
British East India Company's desire for
unrestricted harbor facilities led to the
conclusion of treaties with the sultan of Tajura
as early as 1840. It was not until 1886,
however, that the British gained control over
northern Somalia through treaties with various
Somali chiefs who were guaranteed British
protection. British objectives centered on
safeguarding trade links to the east and
securing local sources of food and provisions
for its coaling station in Aden. The boundary
between Ethiopia and British Somaliland was
established in 1897 through treaty negotiations
between British negotiators and King Menelik.
During the first two decades of this century,
British rule was challenged through persistent
attacks by a dervish rebellion led by Mohamed
Abdullah, known as the "Mad Mullah" by the
British. A long series of intermittent
engagements and truces ended in 1920 when
British warplanes bombed Abdullah's stronghold
at Taleex. Although Abdullah was defeated as
much by rival Somali factions as by British
forces, he was lauded as a popular hero and
stands as a major figure of national identity to
many Somalis.
In 1885, Italy obtained commercial advantages in
the area from the sultan of Zanzibar and in 1889
concluded agreements with the sultans of Obbia
and Aluula, who placed their territories under
Italy's protection. Between 1897 and 1908, Italy
made agreements with the Ethiopians and the
British that marked out the boundaries of
Italian Somaliland. The Italian Government
assumed direct administration, giving the
territory colonial status.
Italian occupation gradually extended inland. In
1924, the Jubaland Province of Kenya, including
the town and port of Kismayo, was ceded to Italy
by the United Kingdom. The subjugation and
occupation of the independent sultanates of
Obbia and Mijertein, begun in 1925, were
completed in 1927. In the late 1920s, Italian
and Somali influence expanded into the Ogaden
region of eastern Ethiopia. Continuing
incursions climaxed in 1935 when Italian forces
launched an offensive that led to the capture of
Addis Ababa and the Italian annexation of
Ethiopia in 1936.
Following Italy's declaration of war on the
United Kingdom in June 1940, Italian troops
overran British Somaliland and drove out the
British garrison. In 1941, British forces began
operations against the Italian East African
Empire and quickly brought the greater part of
Italian Somaliland under British control. From
1941 to 1950, while Somalia was under British
military administration, transition toward
self-government was begun through the
establishment of local courts, planning
committees, and the Protectorate Advisory
Council. In 1948 Britain turned the Ogaden and
neighboring Somali territories over to Ethiopia.
In Article 23 of the 1947 peace treaty, Italy
renounced all rights and titles to Italian
Somaliland. In accordance with treaty
stipulations, on September 15, 1948, the Four
Powers referred the question of disposal of
former Italian colonies to the UN General
Assembly. On November 21, 1949, the General
Assembly adopted a resolution recommending that
Italian Somaliland be placed under an
international trusteeship system for 10 years,
with Italy as the administering authority,
followed by independence for Italian Somaliland.
In 1959, at the request of the Somali
Government, the UN General Assembly advanced the
date of independence from December 2 to July 1,
1960.
Meanwhile, rapid progress toward self-government
was being made in British Somaliland. Elections
for the Legislative Assembly were held in
February 1960, and one of the first acts of the
new legislature was to request that the United
Kingdom grant the area independence so that it
could be united with Italian Somaliland when the
latter became independent. The protectorate
became independent on June 26, 1960; five days
later, on July 1, it joined Italian Somaliland
to form the Somali Republic.
In June 1961, Somalia adopted its first national
constitution in a countrywide referendum, which
provided for a democratic state with a
parliamentary form of government based on
European models. During the early
post-independence period, political parties were
a fluid concept, with one-person political
parties forming before an election, only to
defect to the winning party following the
election. A constitutional conference in
Mogadishu in April 1960, which made the system
of government in the southern Somali trust
territory the basis for the future government
structure of the Somali Republic, resulted in
the concentration of political power in the
former Italian Somalia capital of Mogadishu and
a southern-dominated central government, with
most key government positions occupied by
southern Somalis, producing increased
disenchantment with the union in the former
British-controlled north. Pan-Somali
nationalism, with the goal of uniting the
Somali-populated regions of French Somaliland
(Djibouti), Kenya and Ethiopia into a Greater
Somalia, remained the driving political ideology
in the initial post-independence period. Under
the leadership of Mohamed Ibrahim Egal (prime
minister from 1967 to 1969), however, Somalia
renounced its claims to the Somali-populated
regions of Ethiopia and Kenya, greatly improving
its relations with both countries. Egal
attempted a similar approach with Ethiopia, but
the move towards reconciliation with Ethiopia,
which had been a traditional enemy of Somalia
since the 16thcentury, made many
Somalis furious, including the army. Egal's
reconciliation effort toward Ethiopia is argued
to be one of the principal factors that provoked
a bloodless coup on October 21, 1969 and
subsequent installation of Maj. Gen. Mohamed
Siad Barre as president, bringing an abrupt end
to the process of party-based constitutional
democracy in Somalia.
Following the coup, executive and legislative
power was vested in the 20-member Supreme
Revolutionary Council (SRC), headed by Barre.
The SRC pursued a course of "scientific
socialism" that reflected both ideological and
economic dependence on the Soviet Union. The
government instituted a national security
service, centralized control over information,
and initiated a number of grassroots development
projects. Barre reduced political freedoms and
used military force to seize and redistribute
rich farmlands in the interriverine areas of
southern Somalia, relying on the use of force
and terror against the Somali population to
consolidate his political power base.
The SRC became increasingly radical in foreign
affairs, and in 1974, Somalia and the Soviet
Union concluded a treaty of friendship and
cooperation. As early as 1972, tensions began
increasing along the Somali-Ethiopian border;
these tensions heightened after the accession to
power in Ethiopia in 1973 of the Mengistu Haile
Mariam regime, which turned increasingly toward
the Soviet Union. In the mid-1970s, the Western
Somali Liberation Front (WSLF) began guerrilla
operations in the Ogaden region of Ethiopia.
Following the overthrow of the Ethiopian Emperor
in 1975, Somalia invaded Ethiopia in 1977 in a
second attempt to regain the Ogaden, and the
second attempt initially appeared to be in
Somalia's favor. The SNA moved quickly toward
Harer, Jijiga, and Dire Dawa, the principal
cities of the region. However, following the
Ethiopian revolution, the new Ethiopian
government shifted its alliance from the West to
the Soviet Union, and the Soviet Union supplied
Ethiopia with 10,000-15,000 Cuban troops and
Soviet military advisors during the 1977-78
Ogaden war, shifting the advantage to Ethiopia
and resulting in Somalia's defeat. In November
1977, Barre expelled all Soviet advisers and
abrogated the friendship agreement with the
U.S.S.R. In March 1978, Somali forces retreated
into Somalia; however, the WSLF continued to
carry out sporadic but greatly reduced guerrilla
activity in the Ogaden. Such activities also
were subsequently undertaken by another
dissident group, the Ogaden National Liberation
Front (ONLF).
Following the 1977-1978 Ogaden war, desperate to
find a strong external alliance to replace the
Soviet Union, Somalia abandoned its Socialist
ideology and turned to the West for
international support, military equipment, and
economic aid. In 1978, the United States
reopened the U.S. Agency for International
Development mission in Somalia. Two years later,
an agreement was concluded that gave U.S. forces
access to military facilities at the port of
Berbera in northwestern Somalia. In the summer
of 1982, Ethiopian forces invaded Somalia along
the central border, and the United States
provided two emergency airlifts to help Somalia
defend its territorial integrity. From 1982 to
1988, the United States viewed Somalia as a
partner in defense in the context of the Cold
War. Somali officers of the National Armed
Forces were trained in U.S. military schools in
civilian as well as military subjects.
Following the Ogaden war, the Barre regime
violently suppressed opposition movements and
ethnic groups, particularly the Isaaq clan in
the northern region, using the military and
elite security forces to quash any hint of
rebellion. By the 1980s, an all-out civil war
developed in Somalia. Opposition groups began to
form following the end of the Ogaden war,
beginning in 1979 with a group of dissatisfied
army officers known as the Somali Salvation
Democratic Front (SSDF). In 1981, as a result of
increased northern discontent with the Barre
regime, the Somali National Movement (SNM),
composed mainly of the Isaaq clan, was formed in
Hargeisa with the stated goal of overthrowing of
the Barre regime. In January 1989, the United
Somali Congress (USC), an opposition group of
Somalis from the Hawiye clan, was formed as a
political movement in Rome. A military wing of
the USC was formed in Ethiopia in late 1989
under the leadership of Mohamed Farah "Aideed,"
a former political prisoner imprisoned by Barre
from 1969-75. Aideed also formed alliances with
other opposition groups, including the SNM and
the Somali Patriotic Movement (SPM), an Ogadeen
sub-clan force under Colonel Ahmed Omar Jess in
the Bakool and Bay regions of Southern Somalia.
In 1988, at the President's order, aircraft from
the Somali National Air Force bombed the city of
Hargeisa in northwestern Somalia, the former
capital of British Somaliland, killing nearly
10,000 civilians and insurgents. The warfare in
the northwest sped up the decay already evident
elsewhere in the republic. Economic crisis,
brought on by the cost of anti-insurgency
activities, caused further hardship as Siad
Barre and his cronies looted the national
treasury.
By the end of the 1980s, armed opposition to
Barre's government, fully operational in the
northern regions, had spread to the central and
southern regions. Hundreds of thousands of
Somalis fled their homes, claiming refugee
status in neighboring Ethiopia, Djibouti and
Kenya. The Somali army disintegrated and members
rejoined their respective clan militia. Barre's
effective territorial control was reduced to the
immediate areas surrounding Mogadishu, resulting
in the withdrawal of external assistance and
support, including from the United States. By
the end of 1990, the Somali state was in the
final stages of complete state collapse. In the
first week of December 1990, Barre declared a
state of emergency as USC and SNM forces
advanced toward Mogadishu. In January 1991,
armed opposition factions drove Barre out of
power, resulting in the complete collapse of the
central government. Barre later died in exile in
Nigeria. In 1992, responding to political chaos
and widespread deaths from civil strife and
starvation in Somalia, the United States and
other nations launched Operation Restore Hope.
Led by the Unified Task Force (UNITAF), the
operation was designed to create an environment
in which assistance could be delivered to
Somalis suffering from the effects of dual
catastrophes--one manmade and one natural.
UNITAF was followed by the United Nations
Operation in Somalia (UNOSOM). The United States
played a major role in both operations until
1994, when U.S. forces withdrew.
Following the collapse of the Barre regime in
1991, various groupings of Somali factions
sought to control the national territory (or
portions thereof) and fought small wars with one
another. Approximately 14 national
reconciliation conferences were convened over
the succeeding decade. Efforts at mediation of
the Somali internal dispute were also undertaken
by many regional states. In the mid-1990s,
Ethiopia played host to several Somali peace
conferences and initiated talks at the Ethiopian
city of Sodere, which led to some degree of
agreement between competing factions. The
Governments of Egypt, Yemen, Kenya, and Italy
also have attempted to bring the Somali factions
together. In 1997, the Organization of African
Unity and the Intergovernmental Authority on
Development (IGAD) gave Ethiopia the mandate to
pursue Somali reconciliation. In 2000, Djibouti
hosted a major reconciliation conference (the
13th such effort), which in August resulted in
creation of the Transitional National Government
(TNG), whose 3-year mandate expired in August
2003. The absence of a central government in
Somalia also allowed outside forces to become
more influential by supporting various groups
and persons in Somalia, particularly Djibouti,
Eritrea, Ethiopia, Egypt, Yemen, and Libya, all
of which have supported various Somali factions
and transitional governments.
GOVERNMENT
A transitional government, the components of
which are known as the Transitional Federal
Institutions (TFIs) was formed in 2004 following
the conclusion of a 2-year reconciliation
conference. The TFIs include a transitional
parliament, known as the Transitional Federal
Assembly (formed in August 2004), as well as a
Transitional Federal Government (TFG) that
includes a transitional President, Prime
Minister and a cabinet known as the "Council of
Ministers." For administrative purposes, Somalia
is divided into 18 regions; the nature,
authority, and structure of regional governments
vary, where they exist.
Principal Government Officials
Abdullahi Yusuf Ahmed was elected as
Transitional Federal President of Somalia in
October 2004. On October 29, 2007, Ali Mohamed
Gedi resigned as Prime Minister of the TFG; Nur
"Adde" Hassan Hussein was appointed Prime
Minister on November 22 and confirmed by the
Parliament on November 24, 2007. Following a
no-confidence motion against former Speaker of
Parliament Shariff Hassan Sheikh Adan on January
17, Sheikh Adan Mohamed Nur was elected the new
Speaker on January 31, 2007. A cabinet known as
the Council of Ministers also exists; a new
cabinet of 15 ministers was appointed on January
8, 2008 and approved by Parliament on January
11, 2008.
Other Ministers
Deputy Prime Minister and Minister of
Information--Ahmed Abdisalam Adan
Deputy Prime Minister and Minister of Justice
and Religious Affairs--Salim Aliyow Ebrow
Deputy Prime Minister and Minister of
Education--Aydid Abdullahi Ilkahanaf
Minister of Foreign Affairs and International
Cooperation--Ali Ahmed Jama Jangili
Minister of Finance and Planning--Mohamed Ali
Hamud
Minister of Defense--Muhyadin Mohamed Ali
Minister of National Security and Interior--Muse
Nur Amin
Minister of Regional Development, Federal
Affairs, and Reconciliation--Abdirizal Ashkir
Abdi
Ambassador to the United Nations--Dr. Elmi Ahmed
Duale
Ambassador to the United States--N/A
The self-declared "Republic of Somaliland"
consists of a regional authority based in the
city of Hargeisa, including a President, Vice
President, parliament, and cabinet officials.
POLITICAL CONDITIONS
In early 2002, Kenya organized a reconciliation
effort under IGAD auspices known as the Somalia
National Reconciliation Conference, which
concluded in October 2004. In August 2004, the
Somali Transitional Federal Assembly (TFA) was
established as part of the IGAD-led process.
Abdullahi Yusuf Ahmed was elected President of
the Transitional Federal Government (TFG) of
Somalia on October 10, 2004. The components of
the TFG, including the Parliament and Executive,
are known as the Transitional Federal
Institutions (TFIs).
Two regional administrations exist in northern
Somalia--the self-declared "Republic of
Somaliland" in the northwest and the
semi-autonomous region of Puntland in the
northeast. In Somaliland, which is made up of
the former British protectorate, Dahir Riyale
Kahin was elected President in presidential
elections deemed free and fair by international
observers in May 2003. The area of Puntland
declared itself autonomous (although not
independent) in 1998 with its capital at Garowe.
General Mohamed Adde Muse was elected President
by the Puntland parliament in January 2005.
Puntland declared it would remain autonomous
until a federated Somalia state was established.
ECONOMY
Somalia lacks natural resources and faces
major development challenges, and recent
economic reverses have left its people
increasingly dependent on remittances from
abroad. Its economy is pastoral and
agricultural, with livestock--principally
camels, cattle, sheep, and goats--representing
the main form of wealth. Livestock exports in
recent years have been severely reduced by
periodic bans, ostensibly for concerns of animal
health, by Arabian Peninsula states. Drought has
also impaired agricultural and livestock
production. Because rainfall is scanty and
irregular, farming generally is limited to
certain coastal districts, areas near Hargeisa,
and the Juba and Shabelle River valleys. The
agricultural sector of the economy consists
mainly of banana plantations located in the
south, which has used modern irrigation systems
and up-to-date farm machinery.
A small fishing industry exists in the north
where tuna, shark, and other warm-water fish are
caught, although fishing production is seriously
affected by poaching. Aromatic
woods--frankincense and myrrh--from a small and
diminishing forest also contribute to the
country's exports. Minerals, including uranium
and likely deposits of petroleum and natural
gas, are found throughout the country, but have
not been exploited commercially. Petroleum
exploration efforts have ceased due to
insecurity and instability. Illegal production
in the south of charcoal for export has led to
widespread deforestation. With the help of
foreign aid, small industries such as textiles,
handicrafts, meat processing, and printing are
being established.
The absence of central government authority, as
well as profiteering from counterfeiting, has
rapidly debased Somalia's currency. By the
spring of 2002, the Somali shilling had fallen
to over 30,000 shillings to the U.S. dollar. The
self-declared Republic of Somaliland issues its
own currency, the Somaliland shilling, which is
not accepted outside of the self-declared
republic.
There are no railways in Somalia; internal
transportation is by truck and bus. The national
road system nominally comprises 22,100
kilometers (13,702 mi.) of roads that include
about 2,600 kilometers (1,612 mi.) of
all-weather roads, although most roads have
received little maintenance for years and have
seriously deteriorated.
Air transportation is provided by small air
charter firms and craft used by drug smugglers.
A number of airlines operate from Hargeisa. Some
private airlines, including Daallo Airlines,
serve several domestic locations as well as
Djibouti and the United Arab Emirates. The UN
and other NGOs operate air service for their
missions.
The European Community and the World Bank
jointly financed construction of a deepwater
port at Mogadishu (currently closed). The Soviet
Union improved Somalia's deepwater port at
Berbera in 1969. Facilities at Berbera were
further improved by a U.S. military construction
program completed in 1985, but they have since
become dilapidated. During the 1990s the United
States renovated a deepwater port at Kismayo
that serves the fertile Juba River basin and is
vital to Somalia's banana export industry.
Smaller ports are located at Merca, Brava, and
Bossaso. Absence of security and lack of
maintenance and improvement are major issues at
most Somali ports.
Radiotelephone service is available to both to
regional and international locations. The public
telecommunications system has been destroyed or
dismantled, but cellular phone service is
readily available throughout the country.
Somalia is linked to the outside world via
ship-to-shore communications (INMARSAT) as well
as links to overseas satellite operators by
private telecommunications operators (including
cellular telephone systems) in major towns.
Radio broadcasting stations operate at
Mogadishu, Hargeisa, and Galkaiyo, with programs
in Somali and some other languages. There are
two television broadcast stations in Mogadishu
and one in Hargeisa.
DEFENSE
The Transitional Federal Government and other
various groups throughout Somalia are estimated
to control militias ranging in strength from
hundreds to thousands. Some groups possess
limited inventories of older armored vehicles
and other heavy weapons, and small arms are
prevalent throughout Somalia.
FOREIGN RELATIONS
Somalia followed a foreign policy of
nonalignment for a brief period following
independence. In 1970, the Siad Barre regime
declared a national ideology based on scientific
Socialism and aligned its foreign policy with
the Soviet Union and China. In the 1980s,
Somalia shifted its alignment to the West
following a territorial conflict with Ethiopia
over the disputed Somali-populated region of the
Ogaden from 1977-78, which was supported by the
Soviet Union. The central government also sought
ties with many Arab countries, and continued to
receive financial and military support from
several Arab countries prior to its collapse in
1991.
In 1963, Somalia severed diplomatic relations
with the United Kingdom for a period following a
dispute over Kenya's Somali-populated
northeastern region (Northern Frontier
District), an area inhabited mainly by Somalis.
Related problems have arisen from the boundary
with Ethiopia and the large-scale migrations of
Somali nomads between Ethiopia and Somalia. In
the aftermath of the 1977-78 war between Somalia
and Ethiopia, the Government of Somalia
continued to call for self-determination for
ethnic Somalis living in the Ogaden region of
eastern Ethiopia. At the March 1983 Nonaligned
Movement summit in New Delhi, President Siad
Barre stated that Somalia harbored no
expansionist aims and was willing to negotiate
with Ethiopia over the disputed Ogaden region.
Following the collapse of the Barre regime, the
foreign policy of the various entities in
Somalia, including the Transitional Federal
Government, has centered on gaining
international recognition, winning international
support for national reconciliation, and
obtaining international economic assistance.
U.S.-SOMALI RELATIONS
Although the U.S. never formally severed
diplomatic relations with Somalia, the U.S.
Embassy in Somalia has been closed since the
collapse of the Siad Barre government in 1991.
The United States maintains regular dialogue
with the Transitional Federal Government and
other key stakeholders in Somalia through the
U.S. Embassy in Nairobi, Kenya. Consular
coverage for Somalia also is maintained by U.S.
Embassy Nairobi, while American Citizens
Services in the self-declared Republic of
Somaliland are provided by the U.S. Embassy in
Djibouti.
Principal U.S. Officials
Ambassador to Kenya--Michael
Ranneberger
Special Envoy for Somalia--John M. Yates
Counselor for Somali Affairs--vacant
Political Officer--Mitchell Benedict
Political/Economic Officer--Jessica Davis Ba
Public Affairs Officer--Mark Zimmer
 Information
on Countries from Around the World
Information
on Countries from Around the World Information
on Countries from Around the World
Information
on Countries from Around the World