
PROFILE
OFFICIAL NAME:
Principality of Monaco
Geography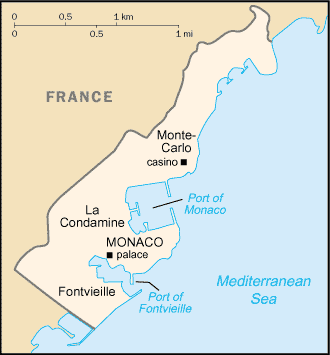
Area: 1.95 sq. km. (0.8 sq. mi); about the size
of New York City's Central Park.
City: Capital--Monaco, pop. 32,409 (July
2005 est.).
Terrain: Hilly.
Climate: Mediterranean.
People
Nationality: Noun and adjective--Monegasque.
Population: 32,409 (July 2005 est.).
Annual growth rate (2005 est.): 0.43%.
Ethnic groups (2003): French 31.95%, Italian
20.02%, Monegasque 19.02%, British 5.32%, Swiss
2.78%, German 2.54%, Belgian 2.46%, American
1.22%, and other 14.7%.
Religions: Roman Catholic 90%, other 10%.
Languages: French (official), English, Italian,
and Monegasque (a blend of French and Italian).
Education: Years compulsory--10, ages
6-16. Attendance--99%. Literacy--99%.
Health (2005 est.): Infant mortality--5.43/1,000.
Life expectancy--75.7 yrs. male; 83.63
yrs. female. Birth rate (July 2005
est.)--9.26 births/1,000 population. Death
rate (July 2005 est.)--12.71 deaths/1,000
population.
Work force (2003, 41,708): Private sector--37,949.
Public sector--3,759. Services--83.5%.
Banking--23.43%. Tourism and hotel--11.64%.
Retail--4.92%. Construction and
public works--32.02%. Industry--6.98%.
Government
Type: Constitutional monarchy.
Constitution: December 17, 1962 (amended in
April 2002).
Branches: Executive--Prince Albert II
(chief of state). Legislative--National
Council (24 members). Judicial--Court of
First Instance, Court of Appeal, High Court of
Appeal, Criminal Court, Supreme Court.
Subdivisions: Four quarters (quartiers)--Monaco-Ville,
La Condamine, Monte-Carlo, Fontvieille.
Political parties: Union pour Monaco (UPM),
National and Democratic Union (UND), Parti
Monégasque (PM).
Suffrage: Universal adult at age 18.
Economy
GDP: Monaco does not publish economic figures
such as gross domestic product, though estimates
placed purchasing power parity GDP at $870
million in 2000.
Avg. annual growth rate (2003 est.): 1.89%.
Per capita purchasing power parity GDP (2000
est.): $27,000.
Agriculture: None.
Industry: Types--tourism, construction,
chemicals, food products, plastics, precision
instruments, cosmetics, ceramics.
Trade: Imports (2003)--about $513 million
(416,348,096 euros). Exports
(2003)--about $644 million (522,976,329 euros).
Currency: Monaco, along with France and the
other 11 members of the European Monetary Union
(EMU), adopted the euro as its official currency
on January 1, 2002. As in other EMU states,
Euros minted in Monaco have special Monegasque
features on one side of the coin.
GEOGRAPHY
The Principality of Monaco is the
second-smallest independent state in the world,
after the Holy See (Vatican City). It is located
on the Mediterranean coast, 18 kilometers (11
mi.) east of Nice, France, and is surrounded on
three sides by France. Monaco is divided into
four sections: Monaco-Ville, the old city on a
rocky promontory extending into the
Mediterranean; La Condamine, the section along
the port; Monte-Carlo, the principal residential
and resort area; and Fontvieille, a newly
constructed area reclaimed from the sea.
The principality is noted for its beautiful
natural scenery and mild, sunny climate. The
average minimum temperature in January and
February is 8oC (47oF); in
July and August the average maximum temperature
is 26oC (78oF).
PEOPLE
In July 2005, Monaco's population was estimated
at 32,409, with an estimated average growth rate
of 0.43%.
French is the official language; English,
Italian, and Monegasque (a blend of French and
Italian) also are spoken. The literacy rate is
99%. Roman Catholicism is the official religion,
with freedom of other religions guaranteed by
the constitution.
HISTORY
Founded in 1215 as a colony of Genoa, Monaco has
been ruled by the House of Grimaldi since 1297,
except when under French control from 1789 to
1814. Designated as a protectorate of Sardinia
from 1815 until 1860 by the Treaty of Vienna,
Monaco's sovereignty was recognized by the
Franco-Monegasque Treaty of 1861. The Prince of
Monaco was an absolute ruler until a
constitution was promulgated in 1911.
In July 1918, a treaty was signed providing
for limited French protection over Monaco. The
treaty, formally noted in the Treaty of
Versailles, established that Monegasque policy
would be aligned with French political,
military, and economic interests.
A new constitution, proclaimed in 1962,
abolished capital punishment, provided for
female suffrage, and established a Supreme Court
to guarantee fundamental liberties.
In 1993, Monaco became an official member of
the United Nations with full voting rights. It
joined the Council of Europe in 2004.
Three months after the death of his father,
Prince Rainier III, on April 6, Prince Albert II
formally acceded to the throne on July 12, 2005.
GOVERNMENT AND POLITICAL CONDITIONS
Monaco has been governed as a constitutional
monarchy since 1911, with the Prince as chief of
state. The executive branch consists of a
Minister of State (head of government), who
presides over a five-member Council of
Government (cabinet). The Minister of State is
responsible for foreign relations. As the
Prince's representative, the Minister of State
also directs the executive services, commands
the police, and presides (with voting powers)
over the Council of Government. The five members
of the Council are respectively responsible for
internal affairs, external affairs, the
environment, finance and economy, and social
affairs and health.
Under the 1962 constitution, the Prince
shares his power with the unicameral National
Council. Sixteen of the 24 members of this
legislative body are elected by list majority
system, and 8 by proportional representation to
serve 5-year terms. The elections were last held
on February 9, 2003, and will be held next in
February 2008. If the Prince dissolves the
National Council, new elections must be held
within 3 months. Usually meeting twice annually,
the Council votes on the budget and endorses
laws proposed by the Prince.
Ordinances passed by the National Council are
debated in the Council of Government, as are the
ministerial decrees signed by the Minister of
State. Once approved, the ordinances must be
submitted to the Prince within 80 days for his
signature, which makes them legally enforceable.
If he does not express opposition within 10 days
of submission, they become valid.
Judicial power is invested in the Prince, who
delegates judicial procedures to the various
courts, which dispense justice in his name. The
independence of the judges is guaranteed by the
constitution. The Supreme Court is composed of
five chief members and two assistant judges
named by the Prince on the basis of nominations
by the National Council and other government
bodies. The Supreme Court is the highest court
for judicial appeals and also interprets the
constitution when necessary. Monaco's legal
system, closely related to that of France, is
patterned after the Napoleonic Code.
The principality's local affairs (the
administration of the four quarters of
Monaco-Ville, La Condamine, Monte Carlo, and
Fontvieille) are directed by the Communal
Council, which consists of 15 elected members
and is presided over by the Mayor.
Principal Government Officials
Chief of State--Prince Albert II, Crown Prince
Minister of State--Jean-Paul Proust
Council of Government
Interior--Philippe Deslandes
Exterior--Rainier Imperti
Finance and Economic Affairs--Franck Biancheri
Social Affairs and Health--Denis Ravera
Environment, Equipment and Urbanism--Giles
Tonelli
National Council President--Stephane Valeri
President of Supreme Court--Roland Drago
Director of Judicial Services--Philippe Narmino
ECONOMY
Monaco, located on the Mediterranean coast, has
an economy primarily geared toward finance,
commerce, and tourism. Low taxes have drawn many
foreign companies to Monaco; the companies’
production accounts for around 50% of the €593
million annual government income (2002). The
enterprises pay a 33.33% tax only if more than
25% of their revenue is generated abroad. Ever
since Monaco’s famed casino opened in 1856, the
tourism industry has been booming. It currently
accounts for close to 25% of the annual revenue.
Customs, postal services, telecommunications,
and banking in Monaco are governed by an
economic and customs union with France. The
official currency is the euro.
Though official economic statistics are not
published, 2000 estimates placed the national
product at $870 million and the per capita
income at $27,000. Monaco does not publish the
figures for unemployment, but in 1998 the rate
was estimated to be at 3.1%.
Monaco is noted for its activity in the field
of marine sciences. Its Oceanographic Museum,
formerly directed by Jacques Cousteau, is one of
the most renowned institutions of its kind in
the world. Monaco imports and exports products
and services from all over the world. There is
no commercial agriculture in Monaco.
FOREIGN RELATIONS
Monaco actively participates in the United
Nations, which it joined in 1993. Monaco joined
the Council of Europe on October 4, 2004. Monaco
also is a member of many international and
intergovernmental organizations, including
Interpol, the UN Educational, Scientific, and
Cultural Organization (UNESCO), and the World
Health Organization (WHO). The International
Hydrographic Bureau (IHB) is headquartered in
Monaco.
The Principality of Monaco is a sovereign and
independent state, linked closely to France by
the Treaty of July 1918, which was formally
noted in Article 436 of the Treaty of Versailles
of 1919. The foreign policy of Monaco is one
illustration of this accord: France has agreed
to defend the independence and sovereignty of
Monaco, while the Monegasque Government has
agreed to exercise its sovereign rights in
conformity with French interests. Since then,
the relations between the sovereign states of
France and Monaco have been further defined in
the Treaty of 1945 and the Agreement of 1963.
In 2002, Monaco renegotiated its 1918 treaty
with France. In 2005 it was ratified by both
parties and entered into force. The terms of the
treaty:
- Upgrade France's representation in
Monaco from Consulate General to that of an
embassy;
- Permit, for the first time, other
countries to accredit ambassadors to Monaco;
and
- Formally recognize the succession scheme
set out in the 1962 Constitution, which
extends eligibility to the Prince's
daughters and other family members.
Although not a member of the European Union (EU),
Monaco is closely associated with the economic
apparatus of the EU through its customs union
with France and its reliance upon the euro as
its official currency.
Monaco has 10 diplomatic missions in Western
Europe and permanent representation at the
United Nations and the Council of Europe. It
maintains honorary consulates in 106 cities in
45 countries. Seventy-four countries have
consulates general, consulates, or honorary
consulates in or accredited to Monaco.
U.S.-MONACO RELATIONS
The United States and Monaco enjoy excellent
relations, which both countries seek to maintain
and strengthen. From 1956 until her death in
1982, the American-born Grace Kelly was married
to Prince Rainier III, Prince Albert’s father.
The United States does not have a diplomatic
mission located in Monaco. The U.S. Consul
General in Marseille, France, under the
authority of the U.S. Ambassador to France, is
formally accredited to Monaco.
Principal U.S. Official
Consul General (Marseille, France)--Philip
Breeden
The
U.S. Consulate General at Marseille is
located at Place Varian Fry, 13286 Marseille
Cedex 6 (tel. [33]-(4)-91-54-92-00).
 Information
on Countries from Around the World
Information
on Countries from Around the World Information
on Countries from Around the World
Information
on Countries from Around the World