
PROFILE
OFFICIAL NAME:
Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan
Geography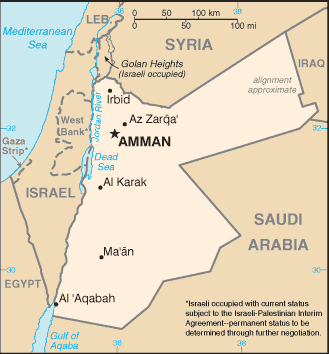
Area: 89,544 sq. km. (34,573 sq. mi.).
Cities: Capital--Amman (pop. 1.9
million). Other cities--Irbid (272,681),
Az-Zarqa (472,830).
People
Nationality: Noun and adjective--Jordanian(s).
Population (2004 census): 5.323 million.
Religions (est.): Sunni Muslim 95%, Christian
4%, Other 1%.
Languages: Arabic (official), English.
Education (2001): Literacy--90%.
Health (2003): Infant mortality rate--19/1,000.
Life expectancy--71 yrs.
Ethnic groups: Mostly Arab but small communities
of Circassians, Armenians, and Kurds.
Work force (1.29 million): Services--83.96%;
industry--12.75%; agriculture--3.29%
Unemployment rate: 13.4%.
Government
Type: Constitutional monarchy.
Independence: May 25, 1946.
Constitution: January 8, 1952.
Branches: Executive--king (chief of
state), prime minister (head of government),
council of ministers (cabinet). Legislative--bicameral
National Assembly (appointed Senate, elected
Chamber of Deputies). Judicial--civil,
religious, special courts.
Political parties: Wide spectrum of parties
legalized in 1992.
Suffrage: Universal at 18.
Administrative subdivisions: Twelve
governorates--Irbid, Jarash, Ajloun, al-'Aqaba,
Madaba, al-Mafraq, al-Zarqa, Amman, al-Balqa,
al-Karak, al-Tafilah, and Ma'an.
Economy
GDP (2004 nominal): $11.515 billion.
Annual growth rate (2004): 7.7%.
Per capita GDP (2004): $2,164.
Natural resources: Phosphate, potash.
Agriculture: Products--fruits,
vegetables, wheat, olive oil, barley, olives.
Land--10% arable; 5% cultivated.
Industry (23.7% of GDP in 2004; 20.7% of GDP in
first half 2005): Types--phosphate
mining, manufacturing, electricity and water;
cement and petroleum production, and
construction.
Trade: Exports--(2004) $3.25 billion;
(Jan-May 2005) $1.4 billion: phosphates, potash,
textiles and garments, fertilizers,
pharmaceutical products, agricultural products.
Major markets--U.S., Iraq, India, Saudi
Arabia, U.A.E., Israel. Imports--(2004)
$8.18 billion; (Jan-May 2005) $3.94 billion:
crude petroleum and derivatives, vehicles,
machinery and equipment, cereals, fabrics and
textiles. Major suppliers--EU, Saudi
Arabia, China, U.S.
Note: From 1949 to 1967, Jordan
administered that part of former mandate
Palestine west of the Jordan River known as the
West Bank. Since the 1967 war, when Israel took
control of this territory, the United States has
considered the West Bank to be territory
occupied by Israel. The United States believes
that the final status of the West Bank can be
determined only through negotiations among the
parties concerned on the basis of UN Security
Council Resolutions 242 and 338.
PEOPLE
Jordanians are Arabs, except for a few small
communities of Circassians, Armenians, and Kurds
which have adapted to Arab culture. The official
language is Arabic, but English is used widely
in commerce and government. About 70% of
Jordan's population is urban; less than 6% of
the rural population is nomadic or seminomadic.
Most people live where the rainfall supports
agriculture. About 1.7 million persons
registered as Palestinian refugees and displaced
persons reside in Jordan, most as citizens.
HISTORY
The land that became Jordan is part of the
richly historical Fertile Crescent region.
Around 2000 B.C., Semitic Amorites settled
around the Jordan River in the area called
Canaan. Subsequent invaders and settlers
included Hittites, Egyptians, Israelites,
Assyrians, Babylonians, Persians, Greeks,
Romans, Arab Muslims, Christian Crusaders,
Mameluks, Ottoman Turks, and, finally, the
British. At the end of World War I, the League
of Nations awarded the territory now comprising
Israel, Jordan, the West Bank, Gaza, and
Jerusalem to the United Kingdom as the mandate
for Palestine and Transjordan. In 1922, the
British divided the mandate by establishing the
semiautonomous Emirate of Transjordan, ruled by
the Hashemite Prince Abdullah, while continuing
the administration of Palestine under a British
High Commissioner. The mandate over Transjordan
ended on May 22, 1946; on May 25, the country
became the independent Hashemite Kingdom of
Transjordan. It ended its special defense treaty
relationship with the United Kingdom in 1957.
Transjordan was one of the Arab states which
moved to assist Palestinian nationalists opposed
to the creation of Israel in May 1948, and took
part in the warfare between the Arab states and
the newly founded State of Israel. The armistice
agreements of April 3, 1949 left Jordan in
control of the West Bank and provided that the
armistice demarcation lines were without
prejudice to future territorial settlements or
boundary lines.
In 1950, the country was renamed the
Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan to include those
portions of Palestine annexed by King Abdullah
I. While recognizing Jordanian administration
over the West Bank, the United States maintained
the position that ultimate sovereignty was
subject to future agreement.
Jordan signed a mutual defense pact in May
1967 with Egypt, and it participated in the June
1967 war between Israel and the Arab states of
Syria, Egypt, and Iraq. During the war, Israel
gained control of the West Bank and all of
Jerusalem. In 1988, Jordan renounced all claims
to the West Bank but retained an administrative
role pending a final settlement, and its 1994
treaty with Israel allowed for a continuing
Jordanian role in Muslim holy places in
Jerusalem. The U.S. Government considers the
West Bank to be territory occupied by Israel and
believes that its final status should be
determined through direct negotiations among the
parties concerned on the basis of UN Security
Council Resolutions 242 and 338.
The 1967 war led to a dramatic increase in
the number of Palestinians living in Jordan. Its
Palestinian refugee population--700,000 in
1966--grew by another 300,000 from the West
Bank. The period following the 1967 war saw an
upsurge in the power and importance of
Palestinian resistance elements (fedayeen) in
Jordan. The heavily armed fedayeen constituted a
growing threat to the sovereignty and security
of the Hashemite state, and open fighting
erupted in June 1970.
No fighting occurred along the 1967 Jordan
River cease-fire line during the October 1973
Arab-Israeli war, but Jordan sent a brigade to
Syria to fight Israeli units on Syrian
territory. Jordan did not participate in the
Gulf war of 1990-91. In 1991, Jordan agreed,
along with Syria, Lebanon, and Palestinian
representatives, to participate in direct peace
negotiations with Israel sponsored by the U.S.
and Russia. It negotiated an end to hostilities
with Israel and signed a peace treaty in 1994.
Jordan has since sought to remain at peace with
all of its neighbors.
GOVERNMENT
Jordan is a constitutional monarchy based on the
constitution promulgated on January 8, 1952.
Executive authority is vested in the king and
his council of ministers. The king signs and
executes all laws. His veto power may be
overridden by a two-thirds vote of both houses
of the National Assembly. He appoints and may
dismiss all judges by decree, approves
amendments to the constitution, declares war,
and commands the armed forces. Cabinet
decisions, court judgments, and the national
currency are issued in his name. The king, who
may dismiss other cabinet members at the prime
minister's request, appoints the council of
ministers, led by a prime minister. The cabinet
is responsible to the Chamber of Deputies on
matters of general policy and can be forced to
resign by a two-thirds vote of "no confidence"
by that body.
Legislative power rests in the bicameral
National Assembly. The number of deputies in the
current Chamber of Deputies is 110, with a
number of seats reserved for various religions,
ethnicities, and women. The Chamber, elected by
universal suffrage to a 4-year term, is subject
to dissolution by the king. The king appoints
the 55-member Senate for a 4-year term.
The constitution provides for three
categories of courts--civil, religious, and
special. Administratively, Jordan is divided
into 12 governorates, each headed by a governor
appointed by the king. They are the sole
authorities for all government departments and
development projects in their respective areas.
Principal Government Officials
Chief of State--King Abdullah bin al-Hussein II
Prime Minister--Adnan Badran
Minister of Defense--Adnan Badran
Foreign Minister--Farouq Al-Qasrawi
Ambassador to the U.S.--Karim Kawar
Ambassador to the UN--Prince Zeid bin Ra'ad
Jordan maintains an
embassy in the United States at 3504
International Drive NW, Washington, DC 20008
(tel. 202-966-2664).
POLITICAL CONDITIONS
King Hussein ruled Jordan from 1953 to 1999,
surviving a number of challenges to his rule,
drawing on the loyalty of his military, and
serving as a symbol of unity and stability for
both the East Bank and Palestinian communities
in Jordan. In 1989 and 1993, Jordan held free
and fair parliamentary elections. Controversial
changes in the election law led Islamist parties
to boycott the 1997 elections. King Hussein
ended martial law in 1991 and legalized
political parties in 1992.
King Abdullah II succeeded his father Hussein
following the latter's death in February 1999.
Abdullah moved quickly to reaffirm Jordan's
peace treaty with Israel and its relations with
the U.S. Abdullah, during his first year in
power, refocused the government's agenda on
economic reform.
Jordan's continuing structural economic
difficulties, burgeoning population, and more
open political environment led to the emergence
of a variety of political parties. Moving toward
greater independence, Jordan's Parliament has
investigated corruption charges against several
regime figures and has become the major forum in
which differing political views, including those
of political Islamists, are expressed. In June
2001, the King dissolved Parliament.
Parliamentary elections were held in June 2003
and municipal elections were held in July 2003.
The King dissolved the government in October
2003, appointing a new Prime Minister and
ushering in three women and several young
technocrats as ministers. The cabinet declared
its commitment to accelerated economic and
political reforms. In April 2005, the King
accepted the resignation of Prime Minister
Faisal Al-Fayez and appointed Adnan Badran in
his place. The King subsequently approved
Badran's formation of a new government, in which
a number of key ministerial posts were
reshuffled.
ECONOMY
Jordan is a small country with limited natural
resources. The country is currently exploring
ways to expand its limited water supply and use
its existing water resources more efficiently,
including through regional cooperation. Jordan
also depends on external sources for the
majority of its energy requirements. During the
1990s, its crude petroleum needs were met
through imports from neighboring Iraq. Since
early 2003, oil has been provided by some Gulf
Cooperation Council member countries. In
addition, a natural gas pipeline from Egypt to
Jordan through the southern port city of Aqaba
is now operational. The first part connecting
Aqaba was completed in 2003. The pipeline was
slated to be operational by late 2005 in the
north to serve the Amman area and beyond. Since
2000, exports of light manufactured products,
principally textiles and garments manufactured
in the Qualifying Industrial Zones (QIZ) that
enter the United States tariff and quota free,
have been driving economic growth. Jordan
exported $6.9 million in goods to the U.S. in
1997, when two-way trade was $395 million; it
exported $1.02 billion in 2004 and $406 million
in the first five months of 2005, with two-way
trade at $1.57 billion and $636 million
respectively. Similar growth in exports to the
United States under the bilateral Free Trade
Agreement that went into effect in December
2001, to the European Union under the bilateral
Association Agreement, and to countries in the
region, holds considerable promise for
diversifying Jordan's economy away from its
traditional reliance on exports of phosphates
and potash, overseas remittances, and foreign
aid. The government has emphasized the
information technology (IT) and tourism sectors
as other promising growth sectors. The low tax
and low regulation Aqaba Special Economic Zone (ASEZ)
is considered a model of a government-provided
framework for private sector-led economic
growth.
The Free Trade Agreement (FTA) with the
United States that went into effect in December
2001 will phase out duties on nearly all goods
and services by 2010. The agreement also
provides for more open markets in
communications, construction, finance, health,
transportation, and services, as well as strict
application of international standards for the
protection of intellectual property. In 1996,
Jordan and the United States signed a civil
aviation agreement that provides for "open
skies" between the two countries, and a
U.S.-Jordan treaty for the protection and
encouragement of bilateral investment entered
into force in 2003. Jordan has been a member of
the World Trade Organization since 2000. More
information on the FTA is available on
www.jordanusfta.com.
Jordan is classified by the World Bank as a
"lower middle income country." The per capita
GDP, as reported by the Government of Jordan,
was $2,164 for 2004, and 13.4% of the
economically active population was unemployed at
the end of 2004. Education and literacy rates
and measures of social well-being are relatively
high compared to other countries with similar
incomes. Jordan's population growth rate is
high, but has declined in recent years, to
approximately 2.2% currently according to the
2004 census preliminary results. One of the most
important factors in the government’s efforts to
improve the well-being of its citizens is the
macroeconomic stability that has been achieved
since the 1990s. Rates of price inflation are
expected to increase (the increase in CPI
averaged 3.4% for 2004), and the currency has
been stable with an exchange rate fixed to the
U.S. dollar since 1995.
While pursuing economic reform and increased
trade, Jordan's economy will continue to be
vulnerable to external shocks and regional
unrest. Without calm in the region, economic
growth seems destined to stay below its
potential.
FOREIGN RELATIONS
Jordan has consistently followed a pro-Western
foreign policy and traditionally has had close
relations with the United States and the United
Kingdom. These relations were damaged by support
in Jordan for Iraq during the first Gulf war.
Although the Government of Jordan stated its
opposition to the Iraqi occupation of Kuwait,
popular support for Iraq was driven by Jordan's
Palestinian community, which favored Saddam as a
champion against Western supporters of Israel.
Following the first Gulf war, Jordan largely
restored its relations with Western countries
through its participation in the Middle East
peace process and enforcement of UN sanctions
against Iraq. Relations between Jordan and the
Gulf countries improved substantially after King
Hussein's death. Following the fall of the Iraqi
regime, Jordan has played a pivotal role in
supporting the restoration of stability and
security to Iraq. The Government of Jordan has
facilitated the training of over 20,000 Iraqi
police cadets at a Jordanian facility near
Amman.
Jordan signed a nonbelligerency agreement
with Israel (the Washington Declaration) in
Washington, DC, on July 25, 1994. Jordan and
Israel signed a historic peace treaty on October
26, 1994, witnessed by President Clinton,
accompanied by Secretary Christopher. The U.S.
has participated with Jordan and Israel in
trilateral development discussions in which key
issues have been water-sharing and security;
cooperation on Jordan Rift Valley development;
infrastructure projects; and trade, finance, and
banking issues. Jordan also participates in
multilateral peace talks. Jordan belongs to the
UN and several of its specialized and related
agencies, including the World Trade Organization
(WTO), the International Meteorological
Organization (IMO), Food and Agriculture
Organization (FAO), International Atomic Energy
Agency (IAEA), and World Health Organization
(WHO). Jordan also is a member of the World
Bank, International Monetary Fund (IMF),
Organization of the Islamic Conference (OIC),
Nonaligned Movement, and Arab League.
Since the outbreak of the Intifada in
September 2000, Jordan has worked hard, in a
variety of fora, to maintain lines of
communication between the Israelis and the
Palestinians to counsel moderation and to return
the parties to negotiations of outstanding
permanent status issues.
U.S.-JORDANIAN RELATIONS
Relations between the U.S. and Jordan have been
close for over four decades. A primary objective
of U.S. policy has been the achievement of a
comprehensive, just, and lasting peace in the
Middle East.
U.S. policy seeks to reinforce Jordan's
commitment to peace, stability, and moderation.
The peace process and Jordan's opposition to
terrorism parallel and indirectly assist wider
U.S. interests. Accordingly, through economic
and military assistance and through close
political cooperation, the United States has
helped Jordan maintain its stability and
prosperity.
Since 1952, the United States has provided
Jordan with economic assistance totaling more
than $9 billion ($1.3 billion in loans and $7.7
billion in grants), including funds for
development projects, health care, education,
construction to increase water availability,
support for microeconomic policy shifts toward a
more completely free market system, and both
grant and loan acquisition of U.S. agriculture
commodities. These programs have been successful
and have contributed to Jordanian stability
while strengthening the bilateral relationship.
U.S. military assistance--provision of material
and training--is designed to meet Jordan’s
legitimate defense needs, including preservation
of border integrity and regional stability.
Principal U.S. Officials
Ambassador--vacant
Charge d’Affaires, a.i.--David M. Hale
Deputy Chief of Mission--Daniel Rubinstein
Political Affairs--Christopher Henzel
Economic Affairs--Richard Eason
Consular Affairs--Daniel Goodspeed
Management Affairs--Perry Adair
Public Affairs--Michael Pelletier
Commercial Counselor--Laurie Farris
The
U.S. Embassy in Jordan is located in Abdoun,
Amman (tel. 962-6-590-6000) and is closed on all
U.S. federal holidays and some Jordanian
holidays. Embassy office hours are Sunday
through Thursday, 8:00 a.m. to 4:30 p.m.
 Information
on Countries from Around the World
Information
on Countries from Around the World Information
on Countries from Around the World
Information
on Countries from Around the World