
PROFILE
OFFICIAL NAME:
Federated States of Micronesia
Geography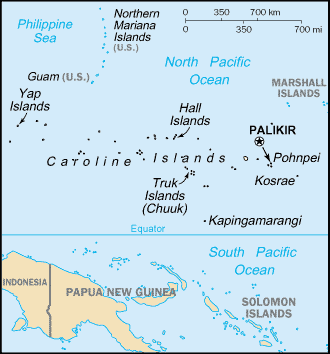
Area: 702 sq. km (about 270 sq. mi.) in four
major island groups/states (Pohnpei, Chuuk, Yap
and Kosrae).
Cities: Capital--Palikir. Other cities--Kolonia,
Moen, Lelu.
Terrain: 607 mountainous islands and low-lying
coral atolls.
Climate: Tropical.
People
Nationality: Noun and adjective--Micronesian.
Population: 107,000.
Growth rate: 3.0%.
Ethnic groups: Nine ethnic Micronesian and
Polynesian groups.
Religion: Roman Catholic 50%, Protestant 47%.
Language: English (official and common), and all
four states have their own ethnic language.
Education: Literacy--89%.
Health: Life expectancy--male 66.7 yrs.;
female 70.6 yrs. Infant mortality rate--33.5/1,000.
Work force: More than one-half of workers are
government employees.
Government
Type: Constitutional confederation in free
association with the U.S. The first Compact of
Free Association entered into force in 1986, and
an Amended Compact entered into force June 30,
2004.
Independence (from U.S.-administered UN
trusteeship): November 3, 1986.
Constitution: May 10, 1979.
Branches: Executive--president (chief of
state and head of government), cabinet.
Legislative--unicameral Congress with 14
seats. Judicial--Supreme Court.
Major political parties: No formal parties.
Economy
GDP: $240 million.
GDP per capita (nominal): $2,200.
National income (GDP + foreign assistance): $360
million.
National income per capita: $3,100.
GDP composition by sector: Services 77%,
agriculture 19%, industry 4%.
Industry: Types--government, fishing.
Trade: Exports ($19 million)--fish,
garments and buttons, betel nut. Export
market--Japan (80%), U.S. Imports
($133 million)--food, manufactured goods, fuel.
Import sources--U.S. (73%), Japan,
Australia.
External debt: $111 million.
Currency: U.S. dollar.
GEOGRAPHY AND PEOPLE
The Federated States of Micronesia (FSM)
consists of 607 islands extending 1,800 miles
across the archipelago of the Caroline Islands
east of the Philippines. The four states are the
island groups of Yap, Chuuk (called Truk until
January 1990), Pohnpei (called Ponape until
November 1984), and Kosrae. The federal capital
is Palikir, on Pohnpei.
The indigenous population, which is
predominantly Micronesian, consists of various
ethnolinguistic groups. English has become the
common language. Population growth remains high
at more than 3%, but the population of the four
states remains almost constant due to
emigration.
HISTORY
The ancestors of the Micronesians settled the
Caroline Islands over 4,000 years ago. A
decentralized chieftain-based system eventually
evolved into a more centralized economic and
religious empire centered on Yap. European
explorers--first the Portuguese in search of the
Spice Islands (Indonesia) and then the
Spanish--reached the Carolines in the 16th
century, with the Spanish establishing
sovereignty. The current FSM passed to German
control in 1899, then to the Japanese in 1914,
and, following World War II, to the United
Nations Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands,
which was administered by the United States
after 1947.
On May 10, 1979, four of the Trust Territory
districts ratified a new constitution to become
the Federated States of Micronesia. The
neighboring trust districts of Palau, the
Marshall Islands, and the Northern Mariana
Islands chose not to participate. The FSM became
independent and signed a Compact of Free
Association with the U.S. in 1986. An Amended
and Perpetual Compact entered into force in June
2004.
GOVERNMENT AND POLITICAL CONDITIONS
The internal workings of FSM are governed by the
1979 constitution, which guarantees fundamental
human rights and establishes a separation of
governmental powers. The unicameral Congress has
14 members elected by popular vote. Four
senators--one from each state--serve 4-year
terms; the remaining 10 senators represent
single-member districts based on population, and
serve 2-year terms. The president and vice
president are elected by Congress from among the
four state-based senators to serve 4-year terms
in the executive branch. Their congressional
seats are then filled by special elections. An
appointed cabinet supports the president and
vice president. There are no formal political
parties.
The FSM is a confederation with a weak
central government. Each of FSM's four states
has its own constitution, elected legislature,
and governor. The state governments maintain
considerable power, particularly regarding the
implementation of budgetary policies.
The judiciary is headed by the Supreme Court,
which is divided into trial and appellate
divisions. The president appoints judges with
the advice and consent of the Congress.
Principal Government Officials
Head of State and Government--President Joseph
J. Urusemal
Secretary of Foreign Affairs--Sebastian L.
Anefal
Speaker of the Congress--Peter Christian
Ambassador to the U.S.--Jesse Marehalau
Permanent Representative to the UN--Masao
Nakayama
FSM maintains an embassy at 1725 N Street NW,
Washington, DC 20036 (tel: 202-223-4383). It
also maintains consulates in Honolulu and Guam.
ECONOMY
Under the terms of the Compact of Free
Association, the U.S. provided FSM with around
$2 billion in grants and services from 1986 to
2001. The Compact's financial terms were
renegotiated for a 20-year period through 2023.
The U.S. will provide almost $100 million in
direct assistance every year until 2023,
including contributions to a jointly managed
Trust Fund. U.S. grants to the FSM in addition
to these funds totaled $57 million in
2004. Assistance under the Amended Compact will
be distributed via grants to the following six
sectors: education, health, infrastructure,
public sector capacity building, private sector
development, and the environment.
The FSM public sector plays a central role in
the economy as the administrator of the Compact
funds. The national and state-level governments
employ over one-half of the country's workers
and provide services accounting for more than
40% of GDP. Real wages nationwide have been flat
for the past decade, as has the number of jobs
in the economy (about 15,500.) Private sector
jobs pay about half as much as public sector
jobs; however, both national and state
government salaries continue to fall in real
terms.
The fishing industry is highly important.
Foreign commercial fishing fleets pay over $20
million annually for the right to operate in FSM
territorial waters. These licensing fees account
for nearly 30% of domestic budgetary revenue.
Additionally, exports of marine products, mainly
re-exports of fish to Japan, account for nearly
85% of export revenue.
Visitor attractions include SCUBA diving in
each state, World War II battle sites, and the
ancient ruined city of Nan Madol on Pohnpei.
Some 15,000 tourists visit the islands each
year. However, the tourist industry has been
hampered by a lack of infrastructure and limited
commercial air connections. The Asian
Development Bank has identified tourism as one
of FSM's highest potential growth industries.
Farming is mainly subsistence, and its
importance is declining. The principal crops are
coconuts, bananas, betel nuts, cassava, and
sweet potatoes. Less than 10% of the formal
labor force and less than 7% of export revenue
come from the agriculture sector. Manufacturing
activity is modest, consisting mainly of two
garment factories in Yap.
The large inflow of official assistance to
FSM allows it to run a substantial trade
deficit--imports outstrip exports by a
seven-to-one ratio--and to have a much lighter
tax burden than other states in the region (11%
of GDP in FSM compared to 18%-25% elsewhere).
The government borrowed against future Compact
disbursements in the early 1990s, yielding a
significant external debt that now tops $60
million. In 2005, the FSM Government and
Congress took positive steps to revamp and
rationalize the nationwide tax system to improve
collections and more fairly distribute the tax
burden.
FOREIGN RELATIONS
The Government of the Federated States of
Micronesia conducts its own foreign relations.
Since independence, the FSM has established
diplomatic relations with a number of nations,
including most of its Pacific neighbors and the
People’s Republic of China. Regional cooperation
through various multilateral organizations is a
key element in its foreign policy. The FSM
became a member of the United Nations in 1991.
U.S.-MICRONESIAN RELATIONS
The Governments of the FSM and the U.S. entered
into the first Compact of Free Association on
November 3, 1986. An Amended Compact entered
into force on June 30, 2004. Under the Compact,
the U.S. has full authority and responsibility
for the defense of the FSM. This security
relationship can be changed or terminated by
mutual agreement. The U.S. will provide $92
million in assistance to the FSM over the next
20 years. A Joint Economic Management Committee
(JEMCO) consisting of representatives of both
nations will ensure that assistance funds are
spent effectively. The basic relationship of
free association continues indefinitely.
Principal U.S. Officials
Ambassador--Suzanne
K. Hale
Deputy Chief of Mission--Stephen Druzak
Management Officer--Michael Pace
The mailing address for the
U.S. Embassy
is P.O. Box 1286, Kolonia, Pohnpei, Federated
States of Micronesia 96941. Telephone:
691-320-2187. Fax: 691-320-2186. Email:
USEmbassy@mail.fm.
 Information
on Countries from Around the World
Information
on Countries from Around the World Information
on Countries from Around the World
Information
on Countries from Around the World