
PROFILE
OFFICIAL NAME:
Republic of Rwanda
Geography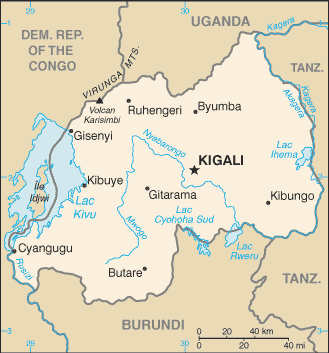
Area: 26,338 sq. km. (10,169 sq. km.); about the
size of Maryland.
Cities: Capital--Kigali
(est. pop. 800,000). Other
cities--Gitarama, Butare, Ruhengeri, Gisenyi.
Terrain: Uplands and hills.
Climate: Mild and temperate, with two rainy
seasons.
People
Nationality: Noun
and adjective--Rwandan(s).
Population (July 2008 est.): approximately
10,180,000.
Annual growth rate (2008 est.): 2.8%.
Ethnic groups: Hutu 85%, Tutsi 14%, Twa 1%.
Religions: Christian 93.5%, traditional African
0.1%, Muslim 4.6%, 1.7% claim no religious
beliefs.
Languages: Kinyarwanda, French, English.
Education: Years
compulsory--6. Attendance--75%
(prewar). Literacy--70.4%.
Health: Infant
mortality rate (2008
est.)--83.4 deaths/1,000. Life
expectancy (2008
est.)--49.8 years.
Work force: Agriculture--90%; industry
and commerce, services, and government--10%
(2000).
Government
Type: Republic.
Independence: July 1, 1962.
Constitution: May 26, 2003.
Branches: Executive--president
(chief of state), prime minister (head of
government). Broad-based government of national
unity formed after the 1994 civil war. Elections
in 2003 elected a president, 80-seat Chamber of
Deputies and 26-member Senate. Legislative--Chamber
of Deputies; Senate. Judicial--Supreme
Court; High Courts of the Republic; Provincial
Courts; District Courts; mediation committees.
Administrative subdivisions: 4 provinces plus
Kigali; 30 districts; 416 sectors; 2,148 cells.
Political parties: There are nine political
parties, including the ruling Rwandan Patriotic
Front (RPF), which leads a coalition that
includes the Centrist Democratic Party (PDC),
the Rwandan Socialist Party (PSR), the Ideal
[formerly Islamic] Democratic Party (PDI), and
the Democratic Popular Union (UPDR). Other
parties include the Social Democratic Party (PSD),
the Liberal Party (PL), the Concord Progressive
Party (PPC), and the Prosperity and Solidarity
Party (PSP).
Suffrage: Universal for citizens over 18--except
refugees, prisoners, and certain categories of
convicts.
Central government budget (2007 est.): 31.7
billions of Rwandan francs ($29 million) Revenues--$28
million. Expenditures--$29
million.
Economy
GDP (2007 est.): $2.8 billion.
Real GDP growth rate (2007 est.): 6.3%.
Per capita income (2006 est.): $260. Purchasing
power parity (2006 est.): $1,600.
Average inflation rate (2007 est.): 9.4%.
Agriculture (2007): 36.2% of GDP. Products--coffee,
tea, pyrethrum (insecticide made from
chrysanthemums), bananas, beans, sorghum,
potatoes, livestock.
Industry (2007): 15.3% of GDP. Types--cement,
agricultural products, beer production, soft
drinks, soap, furniture, shoes, plastic goods,
textiles, cigarettes, pharmaceuticals.
Services (2007): 42.7%.
Trade (2007 est.): Exports--$145
million: tea, coffee, coltan, cassiterite,
hides, iron ore, and tin. Major
markets--China, Belgium, and Germany. Imports (2007
est.)--$488 million f.o.b.: foodstuffs,
machinery and equipment, steel, petroleum
products, cement, and construction material. Major
suppliers--Kenya, Germany, Belgium, France,
Uganda, and Israel.
GEOGRAPHY
Rwanda's countryside is covered by grasslands
and small farms extending over rolling hills,
with areas of rugged mountains that extend
southeast from a chain of volcanoes in the
northwest. The divide between the Congo and Nile
drainage systems extends from north to south
through western Rwanda at an average elevation
of almost 9,000 feet. On the western slopes of
this ridgeline, the land slopes abruptly toward
Lake Kivu and the Ruzizi River valley, which
form the western boundary with the Democratic
Republic of the Congo (formerly Zaire) and
constitute part of the Great Rift valley. The
eastern slopes are more moderate, with rolling
hills extending across central uplands at
gradually reducing altitudes, to the plains,
swamps, and lakes of the eastern border region.
Although located only two degrees south of the
Equator, Rwanda's high elevation makes the
climate temperate. The average daily temperature
near Lake Kivu, at an altitude of 4,800 feet
(1,463 meters) is 73o F
(23o C).
During the two rainy seasons (February-May and
September-December), heavy downpours occur
almost daily, alternating with sunny weather.
Annual rainfall averages 80 centimeters (31 in.)
but is generally heavier in the western and
northwestern mountains than in the eastern
savannas.
PEOPLE
Rwanda's population density, even after the 1994
genocide, is currently the highest in
continental Sub-Saharan Africa. Still a very
rural society, many families live in a
self-contained compound on a hillside. The urban
concentrations are grouped around administrative
centers. The indigenous population consists of
three ethnic groups. Accounts of their
respective arrivals in the area of modern Rwanda
were highly politicized during Rwanda's
post-colonial era, particularly in the years
leading up to the genocide. The Hutus, who
comprise the majority of the population (85%),
are traditionally farmers of Bantu origin. The
Tutsis (14%) are traditionally a pastoral people
who by some accounts arrived in the area in the
15th century. Until 1959, they formed the
dominant caste under a feudal system based on
cattle holding. The Twa (1%) are thought to be
the remnants of the earliest settlers of the
region. Over 70% of the adult population is
literate, but not more than 5% have received
secondary education. During 1994-95, most
primary schools and more than half of prewar
secondary schools reopened. The national
university in Butare reopened in April 1995;
enrollment is over 7,000. Rebuilding the
educational system continues to be a high
priority of the Rwandan Government.
HISTORY
According to folklore, Tutsi cattle breeders
began arriving in the area from the Horn of
Africa in the 15th century and gradually
subjugated the Hutu inhabitants. The Tutsis
established a monarchy headed by a mwami (king)
and a feudal hierarchy of Tutsi nobles and
gentry. However, in some areas of the country,
independent Hutu principalities continued to
exist, and in other areas Tutsi and Hutu
lineages lived in interdependent cooperation
under the nominal control of the Tutsi king.
Within the monarchy, through a contract known as
ubuhake, the Hutu farmers pledged their services
and those of their descendants to a Tutsi lord
in return for the loan of cattle and use of
pastures and arable land. Thus, the Tutsi
reduced some Hutu to virtual serfdom. However,
boundaries of race and class were somewhat
fluid, with most rural Tutsis enjoying few
advantages over the Hutu. The first European
known to have visited Rwanda was German Count
Von Goetzen in 1894. He was followed by
missionaries, notably the "White Fathers." In
1899, the mwami submitted to a German
protectorate without resistance. Belgian troops
from Zaire chased the small number of Germans
out of Rwanda in 1915 and took control of the
country.
After World War I, the League of Nations
mandated Rwanda and its southern neighbor,
Burundi, to Belgium as the territory of
Ruanda-Urundi. Following World War II,
Ruanda-Urundi became a UN Trust Territory with
Belgium as the administrative authority. Reforms
instituted by the Belgians in the 1950s
encouraged the growth of democratic political
institutions but were resisted by the Tutsi
traditionalists who saw in them a threat to
Tutsi rule. An increasingly restive Hutu
population, encouraged by the Belgian military,
sparked a revolt in November 1959, resulting in
the overthrow of the Tutsi monarchy. Two years
later, the Party of the Hutu Emancipation
Movement (PARMEHUTU) won an overwhelming victory
in a UN-supervised referendum.
During the 1959 revolt and its aftermath, more
than 160,000 Tutsis fled to neighboring
countries. The PARMEHUTU government, formed as a
result of the September 1961 election, was
granted internal autonomy by Belgium on January
1, 1962. A June 1962 UN General Assembly
resolution terminated the Belgian trusteeship
and granted full independence to Rwanda (and
Burundi) effective July 1, 1962.
Gregoire Kayibanda, leader of the PARMEHUTU
Party, became Rwanda's first elected president,
leading a one-party government chosen from the
membership of the directly elected unicameral
National Assembly. Peaceful negotiation of
international problems, social and economic
elevation of the masses, and integrated
development of Rwanda were the ideals of the
Kayibanda regime; in reality the Kayibanda
government promoted a Hutu-supremicist ideology.
Relations with 43 countries, including the
United States, were established in the first 10
years. Despite the progress made, inefficiency
and corruption began festering in government
ministries in the mid-1960s. On July 5, 1973,
the military took power under the leadership of
Maj. Gen. Juvenal Habyarimana, who dissolved the
National Assembly and the PARMEHUTU Party and
abolished all political activity.
In 1975, President Habyarimana formed the
National Revolutionary Movement for Development
(MRND) whose goals were to promote peace, unity,
and national development, in the guise of a
one-party state. The movement was organized from
the "hillside" to the national level and
included elected and appointed officials.
Under MRND aegis, Rwandans went to the polls in
December 1978, overwhelmingly endorsed a new
constitution, and confirmed President
Habyarimana as president. President Habyarimana
was re-elected in 1983 and again in 1988, when
he was the sole candidate. Responding to public
pressure for political reform, President
Habyarimana announced in July 1990 his intention
to transform Rwanda's one-party state into a
multi-party democracy.
On October 1, 1990, Rwandan exiles banded
together as the Rwandan Patriotic Front (RPF)
and invaded Rwanda from their base in Uganda.
The rebel force, composed primarily of ethnic
Tutsis, blamed the government for failing to
democratize and resolve the problems of some
500,000 Tutsi refugees living in the diaspora
around the world. The war dragged on for almost
2 years until a cease-fire accord was signed
July 12, 1992, in Arusha, Tanzania, fixing a
timetable for an end to the fighting and
political talks, leading to a peace accord and
power sharing, and authorizing a neutral
military observer group under the auspices of
the Organization for African Unity. A cease-fire
took effect July 31, 1992, and political talks
began August 10, 1992.
On April 6, 1994, the airplane carrying
President Habyarimana and the President of
Burundi was shot down as it prepared to land at
Kigali. Both presidents were killed. As though
the shooting down was a signal, military and
militia groups began rounding up and killing all
Tutsis and political moderates, regardless of
their ethnic background.
The prime minister and her 10 Belgian bodyguards
were among the first victims. The killing
swiftly spread from Kigali to all corners of the
country; between April 6 and the beginning of
July, a genocide of unprecedented swiftness left
up to 800,000 Tutsis and moderate Hutus dead at
the hands of organized bands of militia--Interahamwe.
Even ordinary citizens were called on to kill
their neighbors by local officials and
government-sponsored radio. The president's MRND
Party was implicated in organizing many aspects
of the genocide.
The RPF battalion stationed in Kigali under the
Arusha accords came under attack immediately
after the shooting down of the president's
plane. The battalion fought its way out of
Kigali and joined up with RPF units in the
north. The RPF then resumed its invasion, and
civil war raged concurrently with the genocide
for 2 months. French forces landed in Goma,
Zaire, in June 1994 on a humanitarian mission.
They deployed throughout southwest Rwanda in an
area they called "Zone Turquoise," ostensibly to
quell the genocide and stop the fighting there;
many members of the genocidal rump regime
established after the genocide escaped through
the French zone to eastern Congo. The Rwandan
Army was quickly defeated by the RPF and fled
across the border to Zaire followed by some 2
million refugees who fled to Zaire, Tanzania,
and Burundi. The RPF took Kigali on July 4,
1994, and the war ended on July 16, 1994. The
RPF took control of a country ravaged by war and
genocide. Up to 1 million had been murdered,
another 2 million or so had fled, and another
million or so were displaced internally.
The international community responded with one
of the largest humanitarian relief efforts ever
mounted. The United States was one of the
largest contributors. The UN peacekeeping
operation, UNAMIR, was drawn down during the
fighting but brought back up to strength after
the RPF victory. UNAMIR remained in Rwanda until
March 8, 1996.
Following an uprising by the ethnic Tutsi
Banyamulenge people in eastern Zaire in October
1996, a huge movement of refugees began which
brought more than 600,000 back to Rwanda in the
last 2 weeks of November. This massive
repatriation was followed at the end of December
1996 by the return of another 500,000 from
Tanzania, again in a huge, spontaneous wave.
Less than 100,000 Rwandans are estimated to
remain outside of Rwanda, and they are thought
to be the remnants of the defeated army of the
former genocidal government, its allies in the
civilian militias known as Interahamwe,
and soldiers recruited in the refugee camps
before 1996.
In 2001, the government began implementation of
a grassroots village-level justice system, known
as gacaca,
in order to address the enormous backlog of
cases. Despite periodic prison releases,
including the most recent January 2006 release
of approximately 7,000 prisoners, tens of
thousands of individuals remain in the prison
system, some scheduled to face the traditional
court system, some awaiting trial by gacaca courts,
some convicted by gacaca courts
and returned to serve their sentences. By the
end of 2006, 818,000 genocide suspects had been
identified by the gacaca courts;
case totals are now over one million. These
courts hope to complete their caseload by the
end of 2008.
In January 2008 a moderate earthquake in
neighboring D.R.C., near the southern Rwandan
border town of Cyangugu, caused several dozen
deaths and hundreds of injuries in two Rwandan
districts, with hundreds of homes rendered
uninhabitable and several churches demolished.
Rwandan authorities responded quickly to the
tragedy and, with the assistance of local and
international non-governmental organizations
(NGOs), assisted those in need.
GOVERNMENT AND POLITICAL CONDITIONS
After its military victory in July 1994, the RPF
organized a coalition government similar to that
established by President Habyarimana in 1992.
Called "The Broad Based Government of National
Unity," its fundamental law is based on a
combination of the June 1991 constitution, the
Arusha accords, and political declarations by
the parties. The MRND Party was outlawed. In
April 2003, the transitional National Assembly
recommended the dissolution of the Democratic
Republican Party (MDR), one of eight political
parties participating in the Government of
National Unity since 1994. Human rights groups
noted the subsequent disappearances of political
figures associated with the MDR, including at
least one parliamentarian serving in the
National Assembly. On May 26, 2003, Rwanda
adopted a new constitution that eliminated
reference to ethnicity and set the stage for
presidential and legislative elections in August
and September 2003. The seven remaining
political parties endorsed incumbent Paul Kagame
for president, who was elected to a 7-year term
on August 25, 2003. Rwanda held its first-ever
legislative elections September 29 to October 2,
2003. A ninth political party formed after these
2003 elections. In the spring of 2006, the
government conducted local non-partisan
elections for district mayors and for sector and
cell executive committees. Elections for the
House of Delegates will occur in September 2008.
Challenges facing the government include
promoting further democratization and judicial
reform; completion of prosecution of hundreds of
thousands of individuals for crimes relating to
the 1994 genocide, either by the regular court
system or the gacacasystem;
preventing the recurrence of any insurgency
directed by ex-military and Interahamwe militia
who remain in eastern Congo; and the continuing
work on medium- and long-term development
planning.
Principal Government Officials
President--Paul Kagame
Prime Minister--Bernard Makuza
Minister of Foreign Affairs--Rosemary Musemenali
Ambassador to the United States--James Kimonyo
Ambassador to the United Nations--Joseph
Nsengemana
Rwanda maintains an embassy in
the United States at 1714 New Hampshire Avenue
NW, Washington, DC 20009 (tel. 202-232-2882).
ECONOMY
The Rwandan economy is based on the largely
rain-fed agricultural production of small,
semi-subsistence, and increasingly fragmented
farms. It has few natural resources to exploit
and a small, uncompetitive industrial sector.
While the production of coffee and tea is well
suited to the small farms, steep slopes, and
cool climates of Rwanda, the average family farm
size is one-half hectare, unsuitable for most
agro-business purposes, especially in view of
government ownership of all land and the
resettlement of displaced persons. Agribusiness
accounts for 36.2% (2007 est.) of Rwanda's GDP
and 40.2% of exports. Minerals in 2007 accounted
for 35.9% of export earnings, followed by
tourism, tea and coffee, and pyrethrum (whose
extract is used in insect repellant). Mountain
gorillas and other upscale eco-tourism venues
are increasingly important sources of tourism
revenue. Rwanda's tourism and hospitality sector
requires further development. Rwanda is a member
of the Common Market for Eastern and Southern
Africa (COMESA) and the East African Community.
Some 34% of Rwanda's imports originate in
Africa, 90% from COMESA countries. The
Government of Rwanda has sought to privatize
several key firms. Rwandatel, the government
fixed-line provider and the country's
second-largest mobile phone provider, sold to
American-led Terracom in 2006, was resold to a
Libyan firm in 2007. The government in the last
several years also sold off several
government-owned tea estates, and made great
strides in completing privatization of the
banking sector. Electrogaz, the utility
monopoly, remains to be privatized, as do
several other parastatals.
During the 5 years of civil war that culminated
in the 1994 genocide, GDP declined in 3 out of 5
years, posting a dramatic decline at more than
40% in 1994, the year of the genocide. The 9%
increase in real GDP for 1995, the first postwar
year, signaled the resurgence of economic
activity, due primarily to massive foreign aid.
In the immediate postwar period--mid-1994
through 1995--emergency humanitarian assistance
of more than $307.4 million was largely directed
to relief efforts in Rwanda and in the refugee
camps in neighboring countries where Rwandans
fled during the war. In 1996, humanitarian
relief aid began to shift to reconstruction and
development assistance.
Since 1996, Rwanda has experienced steady
economic recovery, thanks to foreign aid (now
over $500 per year) and governmental reforms.
Since 2002, the GDP growth rate has ranged from
3%-9% per annum, and inflation had ranged
between 2%-9%. Rwanda depends on significant
foreign imports (over $400 million per year).
Exports have increased, up to $145 million in
2007. Private investment remains below
expectations despite an open trade policy, a
favorable investment climate, cheap and abundant
labor, tax incentives to businesses, stable
internal security, and crime rates that are
comparatively low. Investment insurance also is
available through the Africa Trade Insurance
Agency or the Overseas Private Investment
Corporation. The weakness of exports as well as
low domestic savings rates are threats to future
growth.
The Government of Rwanda remains committed to a
strong and enduring economic climate for the
country. To this end the government focuses on
poverty reduction, infrastructure development,
privatization of government-owned assets,
expansion of the export base, and liberalization
of trade. The implementation of a value added
tax of 18% and improved tax collections are
having a positive impact on government revenues
and thereby services rendered. Banking reform
and low corruption also are favorable current
trends. Agricultural reforms, improved farming
methods, and increased use of fertilizers are
improving crop yields and national food supply.
Moreover, the government is pursing educational
and healthcare programs that bode well for the
long-term quality of Rwanda's human resource
skills base.
Many challenges remain for Rwanda. Rwanda is
dependent on significant foreign aid. Exports
continue to lag far behind imports and will
continue to affect the health of the economy.
Inflation may become a problem due to the large
influx of donor funds. The persistent lack of
economic diversification beyond the production
of tea, coffee, and minerals keeps the country
vulnerable to market fluctuations. Rwanda's
landlocked situation necessitates strong highway
infrastructure maintenance, and good transport
linkages to neighboring countries, especially
Uganda and Tanzania, are critical.
Transportation costs remain high and, therefore,
burden import and export costs. Rwanda has no
railway system for port access in Tanzania,
although the nearest railhead from Kigali is 380
kilometers away at Isaka, Tanzania. The
development of small manufacturing and service
industries is needed, and the tourism industry
has far greater potential given the current
stability, travel infrastructure, and available
animal parks as well as other potential tourist
sites. In 2006, Rwanda completed the
Multilateral Debt Relief Initiative and the
Heavily Indebted Poor Countries (HIPC) debt
initiative, significantly lowering its foreign
debt load.
American business interest in Rwanda, other than
in tea and telecommunications, is weak, and the
African Growth and Opportunity Act (AGOA) has
yet to make a significant impact in Rwanda.
Energy needs will stress natural resources in
wood and gas, but hydroelectric power
development is underway, albeit primarily in the
planning stages, as is methane development.
Rwanda does not have nuclear power or coal
resources. Finally, Rwanda's fertility
rate--averaging 5.43 births (2006 est.) per
woman--will continue to stress services, and
diseases such as AIDS/HIV transmission, malaria,
and tuberculosis will have a major impact on
human resources.
Rwanda's government-run radio broadcasts 15
hours a day in Kinyarwanda, English, and French,
the national languages. News programs include
regular re-broadcasts from international radio
such as Voice of America, BBC and Deutsche
Welle. There is one government-operated
television station. In addition to
government-operated Radio Rwanda, there are a
number of independent FM radio stations. There
are few independent newspapers; most newspapers
publish in Kinyarwanda on a weekly, biweekly, or
monthly basis. Several Western nations,
including the United States, are working to
encourage freedom of the press, the free
exchange of ideas, and responsible journalism.
DEFENSE
The military establishment is comprised of a
well-trained army and a small, rotary-wing air
force. Defense spending continues to represent a
disproportionate share of the national budget,
largely due to continuing security problems
along the frontiers with the Democratic Republic
of the Congo and Burundi in the aftermath of the
war. Following withdrawal of Rwandan Armed
Forces from the Democratic Republic of the Congo
in October 2002, the government completely
restructured the military and launched an
ambitious plan to demobilize thousands of
soldiers. At end state, Rwanda will have a
small, well-equipped army of 25,000 soldiers.
FOREIGN RELATIONS
Rwanda is an active member of the international
community and has remained in the international
spotlight since the genocide. Rwanda is an
active member of the UN, having presided over
the Security Council during part of 1995. The UN
assistance mission in Rwanda (UNAMIR), a UN
Chapter Six peacekeeping operation, involved
personnel from more than a dozen countries. Most
of the UN development and humanitarian agencies
have had a large presence in Rwanda. At the
height of the humanitarian emergency, more than
200 nongovernmental organizations were carrying
out humanitarian operations. In addition to
receiving assistance from the international
community, Rwanda has also contributed to
international peacekeeping missions. Currently,
Rwanda Defense Forces (RDF) has deployed four
battalions in support of the UNAMID Mission in
Sudan.
Several west European and African nations,
including Belgium, Canada, China, Egypt, the
United Kingdom, Libya, the Netherlands, Russia,
Sweden, the Holy See, and the European Union
maintain diplomatic missions in Kigali.
In 1998, Rwanda, along with Uganda, invaded the
Democratic Republic of the Congo (D.R.C.) to
back Congolese rebels trying to overthrow
then-President Laurent Kabila. Rwandan troops
pulled out of the D.R.C. in October 2002, in
accordance with the Lusaka cease-fire agreement.
In the fall of 2006, Rwanda broke diplomatic
relations with France, following a French
judge's indictment of senior Rwandan officials
on charges of having participated in the
shooting down of the presidential jet in 1994.
Rwanda rejects these charges. Rwanda, along with
Burundi, joined the East African Community in
2007.
U.S.-RWANDAN RELATIONS
U.S. Government interests have shifted
significantly since the 1994 genocide from a
strictly humanitarian concern focusing on
stability and security to a strong partnership
with the Government of Rwanda focusing on
sustainable development. The largest U.S.
Government programs are the President's
Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR) and the
President's Malaria Initiative, which aim to
reduce the impact of these debilitating diseases
in Rwanda. Other activities promote rural
economic growth and support good governance and
decentralization. Overall U.S. foreign
assistance to Rwanda has increased four-fold
over the past four years.
A major focus of bilateral relations is the U.S.
Agency for International Development's (USAID)
program. In support of the overall Government of
Rwanda development plan, USAID aims to improve
the health and livelihoods of Rwandans and
increase economic and political development. To
achieve this, USAID activities focus on:
- Prevention, treatment and care of
HIV/AIDS;
- Reducing mortality and morbidity due to
malaria;
- Increasing access to, and use of,
voluntary family planning methods;
- Improving maternal and child health;
- Promoting rural economic growth through
specialty coffee, dairy, and eco-tourism;
- Encouraging participatory governance and
decentralization in 12 target districts;
- Promoting a democratic Rwanda, where the
government respects human rights, civil
liberties, and the rule of law; and
- Providing food aid to the most
vulnerable populations.
The Mission is currently implementing a number
of activities related to the goals above, and is
working closely with the Millennium Challenge
Corporation (MCC) to obtain approval of the
Threshold Country Plan submitted by the
Government of Rwanda in November 2007. Once
approved, the plan will be implemented by USAID
and will focus on strengthening the justice
sector and civic participation, and promoting
civil rights and liberties.
The State Department's Public Affairs section
maintains a cultural center in Kigali, which
offers public access to English-language
publications and information on the United
States.
American business interests have been small;
currently, private U.S. investment is limited to
the tea industry, franchising (FedEx, Coca-Cola,
Western Union, and Moneygram) and small holdings
in service and manufacturing concerns. Annual
U.S. exports to Rwanda, under $10 million
annually from 1990-93, exceeded $40 million in
1994 and 1995. Although exports decreased in the
years immediately after the genocide, in 2007
they were estimated at approximately $17
million, a 20% increase over 2006.
Principal U.S. Officials
Ambassador--Michael R. Arietti
Deputy Chief of Mission--Cheryl Sim
Director USAID Program--Dennis Weller
The U.S.
Embassy is
located on 2657 Avenue de la Gendarmerie, Kigali
(tel. 250-596-400, fax 250-596-591).
 Information
on Countries from Around the World
Information
on Countries from Around the World Information
on Countries from Around the World
Information
on Countries from Around the World