
PROFILE
OFFICIAL NAME:
Antigua and Barbuda
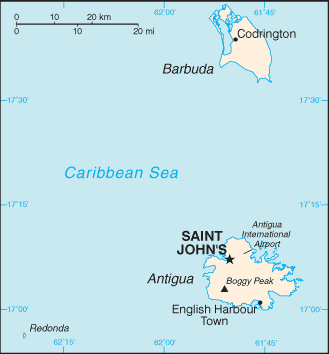
Geography
Area: Antigua--281 sq. km. (108 sq.
mi.); Barbuda--161 sq. km. (62 sq. mi.).
Cities: Capital--St. John's (pop.
30,000).
Terrain: Generally low-lying, with highest
elevation 405 m. (1,330 ft.).
Climate: Tropical maritime.
People
Nationality: Noun and adjective--Antiguan(s),
Barbudan(s).
Population (2004 estimate): 80,039.
Annual population growth rate (2004): 1.9%.
Ethnic groups: Almost entirely of African
origin; some of British, Portuguese, and
Levantine Arab origin.
Religions: Principally Anglican, with
evangelical Protestant and Roman Catholic
minorities.
Language: English.
Education: Years compulsory--9.
Literacy--about 90%.
Health: Life expectancy--71 yrs. male; 75
yrs. female. Infant mortality rate--18/1,000.
Work force (31,300): Commerce and services,
agriculture, other industry.
Unemployment (Labor Commission est. 2002):
11-13%.
Government
Type: Constitutional monarchy with
Westminster-style Parliament.
Constitution: 1981.
Independence: November 1, 1981.
Branches: Executive--governor general
(representing Queen Elizabeth II, head of
state), prime minister (head of government), and
cabinet. Legislative--a 17-member Senate
appointed by the governor general (mainly on the
advice of the prime minister and the leader of
the opposition) and a 17-member popularly
elected House of Representatives. Judicial--magistrate's
courts, Eastern Caribbean Supreme Court (High
Court and Court of Appeals, Privy Council in
London).
Administrative subdivisions: Six parishes and
two dependencies (Barbuda and Redonda).
Political parties: Antigua Labor Party (ALP,
incumbent), United Progressive Party (UPP),
Barbuda People's Movement (BPM).
Suffrage: Universal at 18.
Economy
GDP (2004): $815.2 million.
GDP growth rate (2004): 5.2%.
Per capita GDP (est. 2004): $10,185
Natural resources: Negligible.
Agriculture (2004, 3.2% of GDP): Products--
fish, cotton, livestock, vegetables, and
pineapples.
Services: Tourism, banking, and other financial
services.
Trade: Exports (2004)--$20 million.
Trade partners (2000)--OECS (24%), U.S.
(10%), Trinidad and Tobago (7%), Barbados (21%).
Imports (2004)--$369 million.
Trade partners (2000)--U.S. (27%), U.K.
(10%), OECS (1%).
HISTORY
Antigua was first inhabited by the Siboney
("stone people"), whose settlements date at
least to 2400 BC. The Arawaks--who originated in
Venezuela and gradually migrated up the chain of
islands now called the Lesser
Antilles--succeeded the Siboney. The warlike
Carib people drove the Arawaks from neighboring
islands but apparently did not settle on either
Antigua or Barbuda.
Christopher Columbus landed on the islands in
1493, naming the larger one "Santa Maria de la
Antigua." The English colonized the islands in
1632. Sir Christopher Codrington established the
first large sugar estate in Antigua in 1674, and
leased Barbuda to raise provisions for his
plantations. Barbuda's only town is named after
him. Codrington and others brought slaves from
Africa's west coast to work the plantations.
Antiguan slaves were emancipated in 1834 but
remained economically dependent on the
plantation owners. Economic opportunities for
the new freedmen were limited by a lack of
surplus farming land, no access to credit, and
an economy built on agriculture rather than
manufacturing. Poor labor conditions persisted
until 1939 when a member of a royal commission
urged the formation of a trade union movement.
The Antigua Trades and Labor Union, formed
shortly afterward, became the political vehicle
for Vere Cornwall Bird, who became the union's
president in 1943. The Antigua Labor Party
(ALP), formed by Bird and other trade unionists,
first ran candidates in the 1946 elections and
became the majority party in 1951, beginning a
long history of electoral victories.
Voted out of office in the 1971 general
elections that swept the progressive labor
movement into power, Bird and the ALP returned
to office in 1976, winning renewed mandates in
every subsequent election under Vere Bird’s
leadership until 1994 and also under the
leadership of his son, Lester Bird, up until
March 2004, when the ALP lost power in national
elections.
In the last elections on March 23, 2004, the
United Progressive Party (UPP) gained a 13-seat
majority, while the opposition, now led by Robin
Yearwood, retained four seats.
GOVERNMENT AND POLITICAL CONDITIONS
As head of state, Queen Elizabeth II is
represented in Antigua and Barbuda by a governor
general who acts on the advice of the prime
minister and the cabinet. Antigua and Barbuda
has a bicameral legislature: a 17-member Senate
appointed by the governor general--mainly on the
advice of the prime minister and the leader of
the opposition--and a 17-member popularly
elected House of Representatives. The prime
minister is the leader of the majority party in
the House and conducts affairs of state with the
cabinet. The prime minister and the cabinet are
responsible to the Parliament. Elections must be
held at least every 5 years but may be called by
the prime minister at any time. National
elections were last held on March 23, 2004.
Antigua and Barbuda has a multiparty political
system with a long history of hard-fought
elections, three of which have resulted in
peaceful changes of government.
Constitutional safeguards include freedom of
speech, press, worship, movement, and
association. Antigua and Barbuda is a member of
the eastern Caribbean court system.
Jurisprudence is based on English common law.
Principal Government Officials
Chief of State--Queen Elizabeth II
Governor General--Sir James Carlisle
Prime Minister and Minister of Foreign
Affairs--Winston Baldwin Spencer
Ambassador to the U.S. and the OAS--Deborah Mae
Lowell
Ambassador to the United Nations--Dr. John Ashe
Antigua and Barbuda maintains an embassy in
the United States at 3216 New Mexico Ave. NW,
Washington, DC 20016 (tel. 202-362-5122).
ECONOMY
Antigua and Barbuda's service-based economy grew
by 5.2% in 2004, with tourism, financial
services, and government services as the key
sources of employment and income. Although the
tourism sector faced setbacks from a series of
violent hurricanes since 1995 and a drop off in
tourism after the September 11, 2001 terrorist
attacks, it has largely recovered and had a
strong performance in 2004. More than
three-quarters of a million people visited
Antigua and Barbuda in 2004, the majority from
Europe and the U.S., including over 500,000
cruise ship visitors.
To lessen its vulnerability to natural
disasters and economic shocks, Antigua has
sought to diversify its economy by encouraging
growth in transportation, communications,
Internet gambling, and financial services.
Antigua and Barbuda's currency is the Eastern
Caribbean Dollar (EC$), a regional currency
shared among members of the Eastern Caribbean
Currency Union (ECCU). The Eastern Caribbean
Central Bank (ECCB) issues the EC$, manages
monetary policy, and regulates and supervises
commercial banking activities in its member
countries. The ECCB's primary monetary policy
goal is to maintain the long-standing currency
peg of US$1=EC$2.7.
Antigua and Barbuda is a beneficiary of the
U.S. Caribbean Basin Initiative that grants
duty-free entry into the U.S. for many goods. In
2001, 22% of its total exports of $17 million
went to the U.S. and 28.5% of its $335 million
total imports came from the U.S. Antigua and
Barbuda also belongs to the predominantly
English-speaking Caribbean Community and Common
Market (CARICOM) and the CARICOM Single Market
and Economy (CSME).
FOREIGN RELATIONS
Antigua and Barbuda maintains diplomatic
relations with the United States, Canada, the
United Kingdom, and the People's Republic of
China, as well as with many Latin American
countries and neighboring Eastern Caribbean
states. It is a member of the United Nations,
the Commonwealth of Nations, the Organization of
American States, the Organization of Eastern
Caribbean States, and the Eastern Caribbean's
Regional Security System (RSS).
As a member of CARICOM, Antigua and Barbuda
supported efforts by the United States to
implement UN Security Council Resolution 940,
designed to facilitate the departure of Haiti's
de facto authorities from power. The country
agreed to contribute personnel to the
multinational force, which restored the
democratically elected government of Haiti in
October 1994.
U.S.-ANTIGUA AND BARBUDA RELATIONS
The United States has maintained friendly
relations with Antigua and Barbuda since its
independence. The United States has supported
the Government of Antigua and Barbuda's effort
to expand its economic base and to improve its
citizens' standard of living. However, concerns
over the lack of adequate regulation of the
financial services sector prompted the U.S.
Government to issue a financial advisory for
Antigua and Barbuda in 1999. The advisory was
lifted in 2001, but the U.S. Government
continues to monitor the Government of Antigua
and Barbuda's regulation of financial services.
The U.S. also has been active in supporting
post-hurricane disaster assistance and
rehabilitation through the U.S. Agency for
International Development's (USAID) Office of
Foreign Disaster Assistance and the Peace Corps.
U.S. assistance is primarily channeled through
multilateral agencies such as the World Bank,
the Caribbean Development Bank (CDB), and
through the newly opened USAID satellite office
in Bridgetown, Barbados. In addition, Antigua
and Barbuda receives counter-narcotics
assistance and benefits from U.S. military
exercise-related and humanitarian civic
assistance construction projects.
Antigua and Barbuda is strategically situated
in the Leeward Islands near maritime transport
lanes of major importance to the United States.
Antigua has long hosted a U.S. military
presence. The former U.S. Navy support facility,
turned over to the Government of Antigua and
Barbuda in 1995, is now being developed as a
regional Coast Guard training facility. The U.S.
Space Command continues to maintain a
space-tracking facility on Antigua. The U.S.
Embassy in Antigua closed on June 30, 1994.
Antigua and Barbuda's location close to the
U.S. Virgin Islands and Puerto Rico makes it an
attractive transshipment point for narcotics
traffickers. To address these problems, the U.S.
and Antigua and Barbuda have signed a series of
counter-narcotic and counter-crime treaties and
agreements, including a maritime law enforcement
agreement (1995), subsequently amended to
include overflight and order-to-land provisions
(1996); a bilateral extradition treaty (1996);
and a mutual legal assistance treaty (1996).
In 2004, Antigua and Barbuda had 245,456
stay-over visitors, with around one-third from
the United States. It is estimated that 4,500
Americans reside in the country.
Principal U.S. Embassy Officials
Ambassador--Mary
E. Kramer
Deputy Chief of Mission--Mary Ellen T. Gilroy
Political/Economic Counselor--Sheila Peters
Consul General--Clyde Howard Jr.
Regional Labor Attaché--Alfred Anzaldua
Economic-Commercial Affairs--John Ashworth
Public Affairs Officer--Julie O'Reagan
Peace Corps Director--Terry Armstrong
The United States maintains no official
presence in Antigua. The Ambassador and Embassy
officers are resident in Barbados and travel to
Antigua frequently. However, a U.S. consular
agent resident in Antigua assists U.S. citizens
in Antigua and Barbuda.
The
U.S. Embassy in Barbados is located in
the Canadian Imperial Bank of Commerce Building,
Broad Street, Bridgetown (tel: 246-436-4950;
fax: 246-429-5246). Consular Agent Juliet Ryder
is located at Hospital Hill, English Harbor,
Antigua, tel: (268) 463-6531.
Other Contact Information
U.S. Department of Commerce
International Trade Administration
Office of Latin America and the Caribbean
14th & Constitution Avenue, NW
Washington, DC 20230
Tel: 202-482-1658, 800-USA-Trade
Fax: 202-482-0464
Caribbean/Latin American Action
1818 N Street, NW
Suite 310
Washington, DC 20036
Tel: 202-466-7464
Fax: 202-822-0075  Information
on Countries from Around the World
Information
on Countries from Around the World Information
on Countries from Around the World
Information
on Countries from Around the World