
PROFILE
OFFICIAL NAME:
Republic of Slovenia
Geography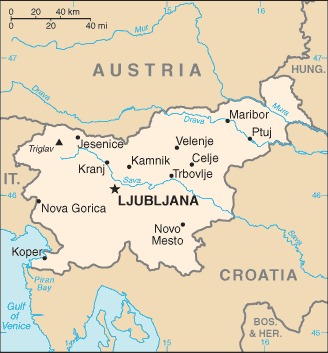
Area: 20,273 square kilometers (7,906 sq. mi.)
slightly smaller than New Jersey.
Cities: Capital--Ljubljana (2002 census
pop. 265,881). Other cities--Maribor
(110,668), Kranj (51,225), Celje (48,081), Koper
(47,539).
Terrain: Mountains rising to more than 2,500
meters (8,200 ft.) in the north, wide plateaus
over 1,000 meters (3,280 ft.) high in the
southeast, Karst limestone region of caves in
the south-southwest, hills in the east, and
approximately 50 kilometers (39 mi.) of
coastline on the Adriatic Sea.
Land use: 54.2% forests, 39% agricultural land,
6.8% noncultivated land.
Climate: Temperate, with regional variations.
Average temperature in the mountain region in
January is below 0°C (32°F), in the interior
from 0°C -2°C (32°F-36°F), and along the coast
from 2°C -4°C (36°F-39°F); in July, average
temperature in the interior is 20°C -22°C
(68°F-72°F), along the coast 22°C -24°C
(72°F-75°F). Average annual rainfall is from 800
mm (31 in.) in the east to 3,000 mm (117 in.) in
the northwest.
People
Nationality: Noun--Slovene(s).
Adjective--Slovenian.
Population (2002 census): 1,987,971. Annual
growth rate: (2003 est.) 0.14%.
Ethnic groups (2002 census): Slovenes 83.06%,
Croats 1.81%, Serbs 1.98%, Bosniaks 1.10%,
Hungarians 0.32%, Montenegrins 0.14%,
Macedonians 0.20%, Albanians 0.31%, Italians
0.11%, Roma 0.17%.
Religions (2002 census): Roman Catholic 57.8%,
refused to reply 15.7%, atheist 10.1%, Orthodox
Christian 2.3%, Muslim 2.4%.
Languages: The official language is Slovene.
Hungarian and Italian are spoken in the border
regions, and German fluency is common near the
Austrian border. Bosnian, Croatian, and Serbian
are spoken by a sizable (6% of the population)
minority. English is widely understood by
business people and students.
Education: Higher education enrollment ratio--26.2%.
Health: Infant mortality rate--4.42/1,000
births. Life expectancy--71.65 years for
men, 79.58 years for women, 75.51 for the total
population.
Work force (2003 est.): 876,100.
Government
Type: Parliamentary democracy.
Independence: On June 25, 1991, the Republic of
Slovenia declared independence from Yugoslavia.
The United States and the European Union
recognized Slovenia in 1992.
Constitution: Adopted on December 23, 1991.
Branches: Executive--president, head of
state, directly elected for a maximum of two
consecutive 5-year terms. Legislative--bicameral
legislature (Parliament is composed of the
National Assembly, with 90 deputies directly
elected on party basis for 4-year terms, and the
National Council, with 40 members elected by the
National Assembly to represent social, economic,
professional, and local interests for 5-year
terms); prime minister, head of government,
nominated by the president and elected by the
National Assembly. Judicial--Constitutional
Court, regular courts, and a public prosecutor.
Political parties: National Assembly
seats--Slovenian Democratic Party (SDS), 29
seats; Liberal Democracy of Slovenia (LDS), 23;
United List of Social Democrats (ZLSD), 10; New
Slovenia - Christian People’s Party (NSi), 9;
Slovene People’s Party (SLS), 7; Slovene
National Party (SNS), 6; Democratic Party of
Slovenian Pensioners (DeSUS), 4; Italian
minority, 1; Hungarian minority, 1.
Suffrage: Universal over 18 years of age;
permanent residents may vote in local elections.
Administrative divisions: 193 local
administrative units.
Government budget: 1.65 trillion SIT (about EUR
6.9 billion or $8.56 billion) (2004); 1.77
trillion SIT (about EUR 7.4 billion or $9.2
billion) (2005); defense, 1.64% GDP (2004).
Economy
GDP (2004): U.S. $32.2 billion.
Real GDP growth rate (2005 est.): 3.8%.
GDP per capita income (2004): U.S. $16,112,
which is approximately 75% of the EU-15 average.
Natural resources: Coal, mercury, timber.
Agriculture/forestry/fishing (approx. 3% of 2004
GDP): Products--wheat, corn, pork,
poultry, milk, potatoes, orchard fruits, wine.
Industry (approx. 36% of 2004 GDP): Types--electrical
equipment, chemical products, textiles, food
products, electricity, metal products, wood
products, transportation equipment.
Services (approx. 60% of 2004 GDP): Types--retail,
transportation, communications, real estate and
other business activities.
Trade: Exports (2004, total U.S. $15.546
billion)--machinery, transportation equipment,
electrical and optical equipment, basic metals
and fabricated products. To U.S.--$619 million
(2004). Imports (2004, U.S. $17
billion)--machinery, transportation equipment,
electrical and optical equipment, basic metals
and fabricated products. From U.S.--$289 million
(2004). Major trading partners--Germany,
Italy, France, Austria, Croatia. Trade with the
U.S. accounts for less than 3% of total trade.
Foreign direct investment: U.S. $6.5 billion
(total stock estimate, end 2004).
GEOGRAPHY AND PEOPLE
Slovenia is situated at the crossroads
of central Europe, the Mediterranean, and the
Balkans. The Alps--including the Julian Alps,
the Kamnik-Savinja Alps, the Karavanke chain,
and the Pohorje Massif--dominate northern
Slovenia near Austria. Slovenia's Adriatic
coastline extends for approximately 50
kilometers (39 mi.) from Italy to Croatia. The
term "karst"--a limestone region of underground
rivers, gorges, and caves--originated in
Slovenia's Karst plateau between Ljubljana and
the Italian border. On the Pannonian plain to
the east and northeast, toward the Croatian and
Hungarian borders, the landscape is essentially
flat. However, the majority of Slovenian terrain
is hilly or mountainous, with around 90% of the
surface 200 meters or more above sea level.
The majority of Slovenia's population is
Slovene (over 83%). Hungarians and Italians have
the status of indigenous minorities under the
Slovenian constitution, which guarantees them
seats in the National Assembly. Most other
minority groups, particularly those from the
former Yugoslavia, immigrated after World War II
for economic reasons. Slovenes are predominantly
Roman Catholic, though the country also has a
small number of Protestants, Orthodox
Christians, Muslims, and Jews. Slovene is a
Slavic language, written in the Roman script.
HISTORY
Slovenia is today a vibrant democracy, but the
roots of this democracy go back deep in Slovene
history. According to the 16th century French
political philosopher, Jean Bodin, Slovenes
practiced the unique custom of the Installation
of the Dukes of Carinthia for almost 1,000
years, until the late 14th century. According to
some scholars, Bodin's account of how Slovene
farmers contractually consented to be governed
by the Duke influenced Thomas Jefferson's
drafting of the Declaration of Independence.
From as early as the 9th century, Slovenia had
fallen under foreign rulers, including partial
control by Bavarian dukes and the Republic of
Venice. With the exception of Napoleon's 4-year
tutelage of parts of Slovenia and Croatia--the
"Illyrian Provinces"--Slovenia was part of the
Habsburg Empire from the 14th century until
1918. Nevertheless, Slovenia resisted
Germanizing influences and retained its unique
Slavic language and culture.
In 1918, Slovenia joined with other southern
Slav states in forming the Kingdom of Serbs,
Croats, and Slovenes as part of the peace plan
at the end of World War I. Renamed in 1929 under
a Serbian monarch, the Kingdom of Yugoslavia
fell to the Axis powers during World War II.
Following communist partisan resistance to
German, Hungarian, and Italian occupation and
elimination of rival resistance groups,
socialist Yugoslavia was born under the helm of
Josip Broz Tito. During the communist era,
Slovenia became Yugoslavia's most prosperous
republic, at the forefront of Yugoslavia's
unique version of communism. Within a few years
of Tito's death in 1980, Belgrade initiated
plans to further concentrate political and
economic power in its hands. Defying the
politicians in Belgrade, Slovenia underwent a
flowering of democracy and an opening of its
society in cultural, civic, and economic realms
to a degree almost unprecedented in the
communist world. In September 1989, the General
Assembly of the Yugoslav Republic of Slovenia
adopted an amendment to its constitution
asserting Slovenia's right to secede from
Yugoslavia. On December 23, 1990, 88% of
Slovenia's population voted for independence in
a referendum, and on June 25, 1990, the Republic
of Slovenia declared its independence. A nearly
bloodless 10-day war with Yugoslavia followed.
Yugoslav forces withdrew after Slovenia
demonstrated stiff resistance to Belgrade.
As a young independent republic, Slovenia
pursued economic stabilization and further
political openness, while emphasizing its
Western outlook and central European heritage.
Reflecting its success in these goals, Slovenia
became a member both of the North Atlantic
Treaty Organization (NATO) and the European
Union (EU) in March and May, respectively, of
2004. As the Organization for Security and
Cooperation in Europe (OSCE) Chairman-in-Office,
a continuing participant in the SFOR/EUFOR
deployment in Bosnia and the KFOR deployment in
Kosovo, one of the top foreign investors in the
former Yugoslavia, and a charter World Trade
Organization (WTO) member, Slovenia enjoys a
growing regional profile and plays a role on the
world stage quite out of proportion to its small
size.
GOVERNMENT AND POLITICAL CONDITIONS
Slovenia enjoys excellent relations with the
United States and cooperates with it actively on
a number of fronts. From 1998 to 2000, Slovenia
occupied a non-permanent seat on the United
Nations (UN) Security Council and in that
capacity distinguished itself with a
constructive, creative, and consensus-oriented
activism. Slovenia has been a member of the UN
since May 1992 and of the Council of Europe
since May 1993. Slovenia signed an association
agreement with the EU in 1996 and became a full
EU member state on May 1, 2004. Slovenia
officially became a member of NATO on March 29,
2004. Slovenia is a member of all major
international financial institutions--the
International Monetary Fund, the World Bank
Group, and the European Bank for Reconstruction
and Development--as well as 40 other
international organizations, among them the WTO,
of which it is a founding member.
Since the breakup of the former Yugoslavia,
Slovenia has instituted a stable, multi-party,
democratic political system, characterized by
regular elections, a free press, and an
excellent human rights record. Slovenia is a
parliamentary democracy and constitutional
republic. Within its government, power is shared
between a directly elected president, a prime
minister, and a bicameral legislature
(Parliament). Parliament is composed of the
90-member National Assembly--which takes the
lead on virtually all legislative issues--and
the National Council, a largely advisory body
composed of representatives from social,
economic, professional, and local interests. The
Constitutional Court has the highest power of
review of legislation to ensure its consistency
with Slovenia's constitution. Its nine judges
are elected by the National Assembly for single
9-year terms.
Slovenia's first President, Milan Kucan,
concluded his second and final term in December
2002. Prime Minister Janez Drnovšek defeated
opposition candidate Barbara Brezigar in the
2002 presidential elections by a comfortable
margin and was inaugurated as Kucan's successor
on December 22, 2002. Finance Minister Anton Rop
succeeded Drnovšek as Prime Minister in December
2002, and his center-left governing coalition
commanded an almost two-thirds majority in the
National Assembly until October 2004. In the
October 2004 election, Janez Jansa’s
center-right Slovenian Democratic Party (SDS)
made a strong showing, winning a relative
majority with over 29% of the vote. Janez Jansa
was sworn in as Prime Minister on November 9,
2004 and the National Assembly confirmed the new
cabinet on December 3.
The government and most of the Slovenian
polity share a common view of the desirability
of a close association with the West,
specifically of membership in both the EU and
NATO. For all the apparent bitterness that
divides left and right wings, there are few
fundamental philosophical differences between
them in the area of public policy. Slovenian
society is built on consensus, which has
converged on a social-democrat model. Political
differences tend to have their roots in the
roles that groups and individuals played during
the years of communist rule and the struggle for
independence.
As the most prosperous republic of the former
Yugoslavia, Slovenia emerged from its brief
10-day war of secession in 1991 as an
independent nation for the first time in its
history. Since that time, the country has made
steady but cautious progress toward developing a
market economy. Economic reforms introduced
shortly after independence led to healthy
economic growth. Despite the halting pace of
reform and signs of slowing gross domestic
product (GDP) growth today, Slovenes now enjoy
the highest per capita income of all the
transition economies of central Europe.
The Slovenes have pursued internal economic
restructuring with caution. The first phase of
privatization (socially-owned property under the
Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, or
S.F.R.Y., system) is now complete. However,
sales of several remaining large state holdings,
planned for several years now, have yet to come
to fruition. The Jansa government has said that
it is committed to seeing this final stage of
privatization happen under its administration.
Foreign trade is very important to the
Slovenian economy, with the annual volume of
imports and exports exceeding 100% of GDP.
Nearly two-thirds of Slovenia’s overall trade is
with the EU and the vast majority of this is
with Germany, Italy, Austria and France. While
the service sector is the largest part of the
economy as a percentage of GDP, manufacturing
accounts for most employment, with machinery and
other manufactured products comprising the major
exports. Labor force surveys put unemployment at
6.4% (2004). Inflation has continued to decline
from 5.6% in 2003 to 3.6% in 2004. Gross
domestic product grew by about 4.6% in 2004 and
is expected to grow at a 3.8% rate in 2005. The
Slovene currency (the tolar, or SIT in
abbreviated form) is stable, fully convertible,
and backed by substantial reserves. In the
coming years, one of Slovenia’s central economic
policy goals is meeting the Maastricht criteria
for adoption of the Euro as Slovenia’s currency.
These criteria include three monetary and two
fiscal measures. As of June 2005, Slovenia was
in line to meet all of these criteria, albeit
inflation is above the current EU limit.
However, the inflation trend is in the right
direction (lower) and barring any major,
unforeseen macroeconomic issues arising,
Slovenia will likely adopt the Euro in 2007.
Over a decade after independence, Slovenia
has made tremendous progress establishing
democratic institutions, enshrining respect for
human rights, establishing a market economy, and
adapting its military to Western norms and
standards. In contrast to its neighbors, civil
tranquility and strong economic growth have
marked this period. Upon achieving independence,
Slovenia offered citizenship to all residents,
regardless of ethnicity or origin, avoiding a
sectarian trap that has caught out many central
European countries. However, debate continues on
how best to accommodate an estimated 18,000
undocumented non-Slovenes who were resident in
Slovenia at the time of independence, but whose
records were "erased" when they did not take
citizenship. Slovenia willingly accepted nearly
100,000 refugees from the fighting in Bosnia and
has since participated in international
stabilization efforts in the region.
On the international front, Slovenia has
advanced rapidly toward integration into the
Euro-Atlantic community of nations. With
successful NATO (66% in favor) and EU (91% in
favor) referenda in March 2003, Slovenia
achieved upon accession in 2004 its two primary
foreign policy goals--membership in the EU and
NATO. Slovenia also participates in the
Stability Pact and the Southeast Europe
Cooperation Initiative (SECI). Slovenia is one
of the focus countries for the U.S. southeast
European policy aimed at reinforcing regional
stability and integration. The Slovenian
Government is well-positioned to be an
influential role model for other southeast
European governments at different stages of
reform and integration. To these ends, the U.S.
urges Slovenia to maintain momentum on internal
economic, political, and legal reforms, while
expanding their international cooperation as
resources allow. U.S. and allied efforts to
assist Slovenia's military restructuring and
modernization efforts are ongoing.
Principal Government Officials
President--Janez Drnovšek
Prime Minister--Janez Jansa
Ambassador to the United States--Samuel Zbogar
Cabinet Ministers
Agriculture, Forestry, and Food--Marija Lukacic
Culture--Vasco Simoniti
Defense--Karl Erjavec
Economy--Andrej Vizjak
Education and Sport--Milan Zver
Environment and Spatial Planning--Janez Podobnik
Finance--Andrej Bajuk
Foreign Affairs--Dimitrij Rupel
Health--Andrej Brucan
Higher Education and Technology--Jurij Zupan
Interior--Dragutin Mate
Justice--Lovro Sturm
Labor, Family and Social Affairs--Janez Drobnic
Public Administration--Gregor Virant
Transport--Janez Bozic
Minister without Portfolio responsible for
Regional Development--(open)
Slovenia maintains an
embassy in the United States at 1525 New
Hampshire Avenue, NW, Washington, DC 20036
(tel.: (202) 667-5363; fax: (202) 667-4563).
ECONOMY
Slovenia enjoys prosperity and stability that
are too often the exception in central and
eastern Europe. Slovenia's economic success
clearly illustrates the benefits of embracing
liberal trade, following the rule of law, and
rewarding enterprise. This success, however, is
not unprecedented for Slovenia. Although it
comprised only about one-thirteenth of
Yugoslavia's total population, it was the most
productive of the Yugoslav republics, accounting
for one-fifth of its GDP and one-third of its
exports. The country already enjoyed a
relatively prosperous economy and strong market
ties to the West when it gained independence in
1991. Since independence, Slovenia has pursued
diversification of its trade toward the West and
integration into Western and transatlantic
institutions vigorously. In so doing, it has
made substantial progress in its transition to a
market economy, particularly becoming party to a
number of bilateral and regional free trade
agreements. Slovenia is a founding member of the
WTO and joined the Central European Free Trade
Agreement (CEFTA) in 1996. Slovenia also
participates in SECI, as well as in the Central
European Initiative, the Royaumont Process, and
the Black Sea Economic Council. Slovenia became
a new EU member state on May 1, 2004.
Today, Slovenia is one the best economic
performers in central and eastern Europe, with a
GDP per capita in 2004 estimated at U.S.
$16,112--slightly more than 75% of the EU-15
average. Slovenia benefits from a well-educated
and productive work force as well as dynamic and
effective political and economic institutions.
Although Slovenia has taken a cautious,
deliberate approach to economic management and
reform, with heavy emphasis on achieving
consensus before proceeding, its overall record
is one of success.
Slovenia has enjoyed healthy growth figures
for the past 8 years, averaging 4.0% annual GDP
growth. The European economic slowdown reduced
the pace of growth somewhat beginning in 2001.
GDP grew by about 4.6% in 2004, and 3.8% growth
is forecast for 2005. Slovenia's economy is
highly dependent on foreign trade. About
two-thirds of Slovenia's trade is with the EU, a
figure which will likely rise following its 2004
accession. Additionally, the country has
penetrated successfully the south and east
European markets, including the former Soviet
Union region. This high level of openness makes
Slovenia extremely sensitive to economic
conditions in its main trading partners and
changes in its international price
competitiveness. Keeping labor costs in line
with productivity is thus a key challenge for
Slovenia's economic well-being. Services
contribute the most to the national output,
accounting for more than 60% of GDP. Industry
and construction comprise over one-third of GDP;
and, agriculture, forestry, and fishing account
for nearly 3% of GDP.
Economic management in Slovenia is relatively
good. Public finances showed modest deficits on
the order of 1.5% of GDP in 2003. The budgets
for 2004 and 2005 constrain public deficit to
1.7% of GDP, well within Maastricht parameters.
The current account balance has improved
significantly as a result of stronger exports
and a changed composition of imports by economic
purpose. In 2003, the current account balance
showed a surplus for the second year in a row.
Based on 11-month data the surplus is estimated
at U.S.$110 million. Controlling inflation
remains a top government priority. While the
authorities have been successful in stabilizing
the Slovenian Tolar and in bringing inflation
down from more than 200% in 1992 to 7.5% in
2002, the end 2004 rate of 3.6% supports the
government’s plan for meeting Maastricht
criteria in two years.
Due to its macroeconomic stability, favorable
foreign debt position, and successful accession
to the EU, Slovenia consistently receives the
highest credit rating of all transition
economies--receiving the top regional honors in
a recent Dunn & Bradstreet survey. Slovenia's
ability to meet its growth rate objectives will
largely depend on the state of the world
economy, since exports demand in Slovenia's
primary market has stalled. Foreign direct
investment (FDI) will take up the slack to some
extent, as analysts forecast FDI levels will
continue to increase with further privatization
of state assets, including portions of the
telecommunications, financial, and energy
sectors. Slovenia must carefully address fiscal,
monetary, and FDI policy, in light of the high
deficit in pension accounts, its vulnerable
Western export markets, and inflation concerns.
Slovenian enterprises have a tradition of market
orientation that has served them well in the
transition period, as they moved energetically
to reorient trade from former Yugoslav markets
to those of central and eastern Europe. However,
in many cases under the Slovenian brand of
privatization, managers and workers in formerly
"socially owned" enterprises have become the
majority shareholders, perpetuating the
practices of "worker management" that were the
hallmark of the Yugoslav brand of communism.
Difficulties associated with that model are
expected to decrease under competitive
pressures, as shares in these firms change
hands, and as EU reforms introduce more
Western-oriented governance practices.
Slovenia's entry into the European Union
provides the impetus for further economic
improvements. Economic policy is geared largely
toward EU integration. The government continues
to focus on adopting EU rules on the internal
market, structural economic reform, reform of
the judiciary and public administration, and
introduction of E-administration. Harmonization
with EU laws and regulations will remain a major
challenge to the government in the near future.
Slovenia's position with respect to other
central and eastern European (CEE) countries
will decline without further vigorous reforms.
Slovenia has taken some important steps in
recent years to free up its financial markets.
This sector historically has been one of the
most protected, reflecting Slovenian concerns
over limited capacity to face global competition
and a desire to maintain domestic control over
finance. A combination of market forces, changes
in Bank of Slovenia regulations, and national
legislation are moving this sector increasingly
in a more globally oriented direction. In 2003,
several measures were introduced to make both
portfolio and direct investments easier and more
transparent in Slovenia and to conduct many
financial operations, including banking,
securities brokering, and undertaking various
credit transactions. Most remaining barriers
were removed by May 1, 2004. For instance,
marketing of foreign mutual investment funds is
allowed as of May 1, 2004. The banking sector
also is showing signs of stirring from its
relative inactivity, as pressures build to
consolidate Slovenia's myriad banks build and as
privatization of two of the largest banks
proceeds. While Belgian KBC is the main owner of
Nova Ljubljanska Banka (NLB) with 34%, little
progress has been made in the privatization of
NKBM bank, Slovenia’s largest bank. The
government continues to downsize state shares in
the insurance sector; however, the
government-owned Triglav still controls nearly
half of the insurance market. Other insurance
companies have been privatized or are
foreign-owned.
Government efforts and reforms designed to
attract foreign direct investment (FDI) have
proven successful--FDI almost tripled from 2001
to 2002, accounting for nearly 6.5% of GDP.
However, FDI fell sharply in 2003 due to a lack
of any major privatization deal or foreign
acquisition. Slovenia's traditional
anti-inflation policy in the past relied heavily
on capital inflow restrictions. Its slow
privatization process favored domestic investors
and prescribed long lag time on share trading,
complicated by a cultural wariness of being
"bought up" by foreigners. As such, Slovenia has
had a number of impediments to full foreign
participation in its economy. However, a number
of these barriers to FDI were fully removed in
2002. As a result, expected foreign takeovers of
Slovenian blue chip companies, as well as EU
membership, have fueled investors' interest in
the country. Recent acquisitions by
multinational companies--KBC of Belgium's
takeover of Nova Ljubljanska Banka, and Swiss
Novartis' takeover of Lek
Pharmaceuticals--clearly demonstrate the
attractiveness of the Slovenian economy,
particularly to European investors seeking a
platform to support expansion into southeastern
Europe. U.S. investments in Slovenia have been
more modest, Goodyear and Western Wireless
International being the two largest American
investors. Removal of administrative barriers,
further liberalization of the financial sector,
completion of privatization, and progress on
company restructuring are necessary to improve
economic performance at the macro and micro
levels. Without these measures, employment and
FDI figures may not reach their full capacity.
DEFENSE
Slovenian Armed Forces
After successful resistance to the Yugoslav
National Army (JNA) following the 10-day war of
independence in 1991, Slovenia faced the
challenge of establishing independent armed
forces. A major reorganization of the Slovene
Armed Forces is currently underway, with the
goal of changing from a conscription-based
territorial defense force to a professional,
deployable, and combat capable military with
NATO. Conscription ended earlier than expected,
in October 2003, and compulsory reserve service
will end by 2010. As of August 2004, Slovenia’s
professional force included 6,800 soldiers and
nearly 14,000 reservists. The current force
structure consists of one fully professional
motorized infantry brigade and two cadre/reserve
force mechanized brigades. The professional
brigade represents Slovenia's deployable
reaction force. The Slovene Armed Forces also
include a small air force, equipped with
helicopters and turbo-prop fixed wing aircraft,
and a naval attachment, including a coastal
patrol boat. The United States provides
bilateral military assistance to Slovenia,
including through the International Military
Education and Training (IMET) program, the
Foreign Military Financing (FMF) program, the
State Partnership Program (aligned with
Colorado), the George C. Marshall European
Center for Security Studies, and the EUCOM Joint
Contact Team Program
NATO
After receiving an invitation to join NATO at
the NATO Prague Summit in November 2002,
Slovenes approved NATO accession with a vote of
66% in a March 2003 referendum. The National
Assembly ratified accession to the North
Atlantic Treaty in February 2004, and Slovenia
officially became a member of the Alliance on
March 29, 2004. After gaining independence,
Slovenia avidly sought NATO membership as part
of its overall strategy of integration into the
most important international economic,
financial, and security organizations.
Slovenia's current international commitments
show Slovenia's willingness to become a
co-provider of security in the region. Slovenia
contributed helicopters, medical personnel,
military police, and an infantry company to SFOR
and continues to be very active in EUFOR with
210 troops deployed in Bosnia and Herzegovina.
In Kosovo, Slovenia actively participates in
KFOR with 34 troops. In March 2004, Slovenia
sent a detachment of special operations troops,
along with some vehicles, to the ISAF mission in
Afghanistan. A second rotation was sent in
August 2004, followed by two firefighters to
guard the Kabul Airport in September 2004. In
July 2005, an additional 29 troops were deployed
to the ISAF mission in Herat, bringing the total
number of Slovenian personnel in ISAF to 60.
The Government of Slovenia has diligently
pursued its restructuring, reorganization,
modernization, and procurement with the
paramount goal of NATO interoperability. The
United States has encouraged Slovenia to
maintain the pace of reform--including the
establishment of closer links with regional
partners--even following its attainment of full
membership in NATO.
FOREIGN RELATIONS AND REGIONAL COOPERATION
In regular public statements, Slovenia's highest
politicians underscore their government's
commitment to expanding cooperative arrangements
with neighbors and active contributions to
international efforts aimed at bringing
stability to southeast Europe. Resource
limitations are a concern for the government,
which does not wish to see itself spread too
thin. Nonetheless, the Slovenes are taking
concrete steps toward a more outward looking and
constructive role in regional security
arrangements, as resources allow.
Multilateral
- Slovenia assumed its duties as
Chairman-in-Office of the OSCE in January
2005. Slovenia is a member of the OSCE
Troika along with Bulgaria and Belgium,
which will fill the CiO slot in 2006.
- Through its International Trust Fund for
Demining and Mine Victims Assistance (ITF),
Slovenia has created the demining instrument
of choice for the international community in
Bosnia and Herzegovina, the rest of the
Balkans, and now even further afield in
Central Asia and Cyprus. The United States
has contributed over $82 million to the ITF
since 1998.
- Slovenia is engaged with 29 countries in
bilateral military exchange--most actively
with the U.S.--and in regional cooperative
arrangements in central and southeast
Europe; it participates in or intends to
contribute forces for five major
multinational regional peacekeeping bodies.
- Slovenia participates in the
Proliferation Security Initiative (PSI) to
halt the proliferation of weapons of mass
destruction (WMD), their delivery systems,
and related materials worldwide.
- Slovenia has ratified all thirteen
international anti-terrorism conventions.
- Slovenia is party to the Wassenaar
arrangement controlling exports of weapons
and sensitive technology to countries of
concern.
- With Hungary and Italy, Slovenia formed
a Multinational Land Force (Trilateral
Brigade) in April 1998 with regional
peacekeeping ability. Further nonmilitary
cooperation within the Trilateral Brigade
occurs in the fields of transportation
infrastructure, combating money laundering
and organized crime, weapons of mass
destruction (WMD) non-proliferation, border
controls, and environmental protection. In
2001, Croatia was invited to join what then
became the Quadrilateral Brigade.
- Slovenia's 10th motorized infantry
battalion, established in 1996 as its
primary "out-of-country" operation unit, is
fully operational; one company was deployed
to SFOR (now EUFOR) in January 2003.
- Slovenia is an active participant in
Southeast European Defense Ministerial (SEDM)
activities.
Contributions to Bosnian Stability
- Slovenia has been engaged in both the
SFOR and EUFOR missions, providing VIP
support helicopter and light transport
aircraft missions and use of an airbase in
southern Slovenia.
- Slovenia currently has a total of 210
personnel in Bosnia and Herzegovina,
including a platoon of military police (up
to 48) for the Italian-led Multinational
Specialized Unit (MSU) in Sarajevo which has
been deployed since January 1999.
- Slovenia contributes to mine action
programs in Bosnia and Herzegovina through
the ITF.
Relations With Neighbors
Slovenia's bilateral relations with its
neighbors are generally harmonious and
cooperative. However, there remain a few
unresolved disputes with Croatia related to the
succession of the former Yugoslavia, including
demarcation of their common border. In addition,
unlike the other successor states of the former
Yugoslavia, Slovenia did not normalize relations
with Serbia and Montenegro until after the
passing from power of Slobodan Milosevic
(although the Slovenes did open a representative
office in Podgorica to work with Montenegrin
President Djukanovic's government).
With its entry into the European Union,
Slovenia has become a strong advocate for the
inclusion of other former Yugoslav republics
into Euro-Atlantic institutions. Slovenia's
strong political ties to the region are
complemented by strong economic ties. Slovenia
is among the largest foreign investors in the
region.
Italy. Italian-Slovene bilateral
relations are also very good. By mid-1996,
property restitution disputes derived from World
War II had been set aside, allowing a dramatic
improvement in relations. In 2001, the Italian
Senate voted final approval of legislation
resolving some minor differences remaining over
minority rights issues and over the compensation
for property abandoned by Italian refugees
fleeing communist Yugoslavia in the postwar
period.
Hungary. Relations are excellent with
Hungary. Hungarian (as well as Italian)
minorities in Slovenia are accorded special
treatment under the Slovenian constitution,
including a permanent parliamentary seat. Within
the Multilateral Cooperation Initiative between
Slovenia, Italy, Hungary, and Croatia,
cooperation exists in numerous fields, including
military (Multinational Land Force peacekeeping
brigade), transportation, combating money
laundering and organized crime,
non-proliferation, border crossings, and
environmental issues.
Austria. Austro-Slovenian relations
are close. Although some disagreements over
support for the other country's minorities
continue to flare up, they are usually handled
diplomatically and in a straightforward manner.
Questions regarding nuclear power in Slovenia
and the basis for the settlement of the Austrian
State Treaty also appear to have been solved.
Economic cooperation is expanding, including a
joint project for development of border regions.
Croatia. Though somewhat rocky at
times, Croatian-Slovenian relations are solid.
Outstanding issues include a few remaining
border disputes, property rights, and Croatian
depositors' savings in the Ljubljanska Banka
from Yugoslav times. In 2003, Croatia declared
its intention to claim a 200-mile exclusive
economic zone in the Adriatic Sea, which would
effectively cut off Slovenia’s use of
international waters. Multilateral discussions
among Slovenia, Croatia, and Italy on this issue
continue with European Commission participation.
In a series of high-level meetings since the
latter half of 1998, Slovenia and Croatia have
been engaged in settling bilateral differences,
a process which accelerated after the death of
Croatian President Franjo Tudjman in 1999 and
has intensified under the government of Prime
Minister Janez Jansa elected in October 2004. In
order to aid the stabilization of this part of
Europe, Slovenia has supported Croatia's efforts
to draw closer to European institutions.
Slovenia and Croatia most recently made an
effort to improve relations during a joint
government session on June 10, 2005 where three
bilateral agreements were signed: Joint
Statement on Avoiding of Conflicts, Bilateral
Agreement on Avoiding Double Taxation, and an
establishment of a joint Historical Commission
for the border issue.
U.S.-SLOVENIAN RELATIONS
Since Slovenia achieved its independence in 1991
the United States and Slovenia have developed
strong, cooperative relations on a broad range
of issues, from promoting regional security to
developing closer bilateral trade and investment
ties. The U.S. was very supportive of Slovenia's
entrance into NATO and other Euro-Atlantic
agreements and institutions.
The first official U.S. presence in Slovenia
dates from the early 1970s, when the United
States Information Service (USIS) opened a
library and American press and cultural center
in Ljubljana. From its opening through 1992, the
American Center worked to develop closer
grassroots relations between the United States
and the people of the then-Slovenian Republic of
Yugoslavia.
On December 23, 1990, the Slovene people
voted in a plebiscite to separate from greater
Yugoslavia. On June 25, 1991, the new Republic
of Slovenia officially declared its independence
from the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. A
10-day war commenced, during which Slovenian
territorial troops fought off incursions by the
Yugoslav National Army. The United States
formally recognized the new republic on April 7,
1992. To develop U.S. diplomatic relations with
the new state, the United States opened a new
Embassy in Ljubljana in August 1992.
Since 1992, the United States and the
Republic of Slovenia have developed an
impressive track record of cooperation on
bilateral, regional, and global issues. The
United States has worked closely with the
Slovenes to resolve succession issues stemming
from the breakup of Yugoslavia. Slovenia
provided invaluable assistance to the United
States and NATO by facilitating the deployment
of IFOR--and subsequently SFOR--to Bosnia after
the conclusion of the Dayton accords. With
strong U.S. support, Slovenia has developed the
ITF as the demining instrument of choice in the
Balkans and is expanding operations to include
the Caucasus.
On the economic front, the United States has
worked to develop bilateral trade and investment
with Slovenia. U.S. trade (imports and exports)
with Slovenia for 2004 was $908 million. Under
the Support for Eastern European Democracy
(SEED) Act, the U.S. provided technical
assistance on enterprise competitiveness,
banking and pension reform, competition policy,
and debt restructuring. Reflecting the progress
Slovenia has made in these areas, Slovenia was
among the first transition countries to
"graduate" from the SEED program.
The United States supported Slovenia's
accession to the North Atlantic Alliance and
continues to work with the Slovenian military to
promote greater cooperation and interoperability
with NATO forces. The United States and Slovenia
hold periodic high-level security consultations
to help Slovenia achieve this national
objective. The U.S. European Command provides a
liaison team that works with the Ministry of
Defense full-time to develop greater familiarity
with NATO structures and procedures.
In addition to regular diplomatic relations,
numerous top-level visits on both sides have
strengthened bilateral dialogue and contributed
to deepening relations. President Bush met with
then-President Milan Kucan and then-Prime
Minister Janez Drnovšek in Slovenia during the
June 2001 summit between President Bush and
Russian President Putin. Then-Prime Minister
Drnovšek met again with President Bush in
Washington in May 2002. Defense Minister Anton
Grizold and Foreign Minister Dimitrij Rupel
traveled to Washington in September 2002.
Secretary of Defense Donald Rumsfeld visited
Ljubljana in November 2002, following the NATO
summit in Prague. Speaker of the House Dennis
Hastert traveled to Ljubljana in September 2003.
In October 1997, Slovenia joined the group of
countries--now numbering 27--whose citizens
enjoy the privilege of visa-free travel to the
United States. Having become a NATO member in
2004, Slovenia hosted a session of the NATO
Parliamentary Assembly in May 2005. Also,
Foreign Minister Rupel has met with Secretary
Rice several times in 2005 as the chairman of
OSCE, most recently in July.
Given Slovenia's relative economic success
and location, its history, language, business
ties, and insights into the region, Slovenia can
be a partner in advancing the shared goal of
regional political and economic stability. More
than geographically, Slovenia is a bridge from
developed Europe into the Balkans, an area of
the continent that poses significant diplomatic
and security challenges.
Principal U.S. Official
Ambassador--Thomas
Bolling Robertson
The
U.S. Embassy in Slovenia is located at
Prešernova 31, 1000 Ljubljana (tel.: +386 (1)
2005500; fax: +386 (1) 200-5555).
 Information
on Countries from Around the World
Information
on Countries from Around the World Information
on Countries from Around the World
Information
on Countries from Around the World